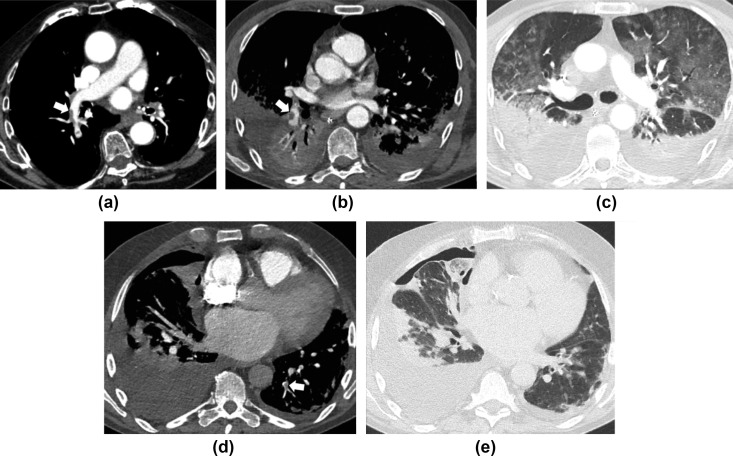
Figure 2.
Embolisms in the lobar, segmental, and subsegmental pulmonary arteries in three COVID-19 patients. (a) CT pulmonary angiogram of a 74-year-old man with D-Dimer level >800 ng/ml on admission reveals thrombus (arrow) in the right lobar pulmonary artery for the inferior lobe. (b,c) A 63-year-old man on day 23 after admission and D-dimer level of 15,662 ng/ml. CT pulmonary angiogram reveals pulmonary thrombus (arrow) in the right segmental pulmonary artery for the basal pyramid, bilateral pleural effusion with atelectasis, consolidations in the posterior segments of the inferior lobes (gravitational segments), and ground-glass opacities in the anterior segments (anti-gravitational segments), consistent with acute respiratory distress syndrome. (d,e) A 79-year-old man on day 1 after admission and D-dimer level of 54,158 ng/ml with pulmonary thrombus (arrow) in the subsegmental pulmonary artery for the postero-basal segment of the left inferior lobe, bilateral pleural effusion with consolidations and pneumothorax on the right side.