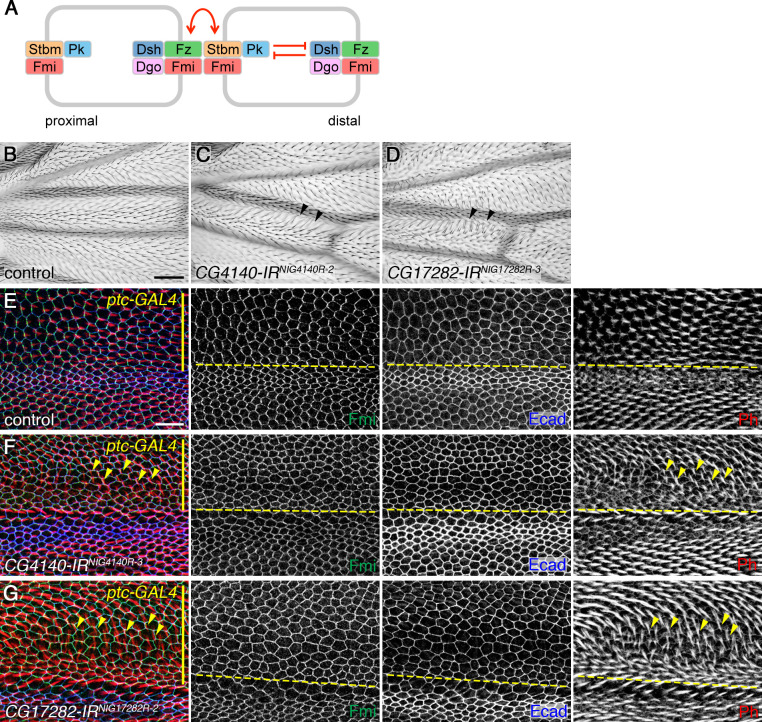
Fig 1. RNAi knockdown of DAnkrd49 and Bdbt disrupts planar polarity.
(A) Diagram to illustrate asymmetric localisation of the core planar polarity proteins. Fz, Dsh and Dgo localise to distal cell ends, while Stbm and Pk localise proximally and Fmi localises both proximally and distally. Feedback interactions are thought to lead to mutual inhibition between proximal and distal complex components (red inhibitory lines), while intercellular interactions between proximal and distal components are thought to stabilise asymmetric complexes (red arrows). (B-D) Dorsal surface of adult male wings from control wild-type flies (B), or from flies expressing RNAi against CG4140/DAnkrd49 (C, NIG line 4140R-2), or CG17282/Bdbt (D, NIG line 17282R-3), under control of the MS1096-GAL4 driver at 25°C. Distal is to the right and anterior is up in these and all other images. Black arrowheads mark a proximal region of the wing, between veins 3 and 4, in which trichomes point distally in wild-type wings, but swirl anteriorly in DAnkrd49 and Bdbt knockdown wings. Note that anterior to vein 3, trichomes tend to point towards the vein in wild-type as well as in mutants wings. Scale bar 50 μm. (E-G) Pupal wings expressing a control RNAi (E, VDRC line 39864, targeting Sik1, a gene unrelated to planar polarity), or RNAi against CG4140/DAnkrd49 (F, NIG line 4140R-3), or CG17282/Bdbt (G, NIG line 17282R-2), under control of the ptc-GAL4 driver. Larvae were raised at 25°C, collected as white prepupae and then aged for 27hr at 29°C. Wings immunolabelled for Fmi (green) and Ecad (blue), and trichomes labelled with Phalloidin (red). ptc-GAL4 is expressed at the top of the image (yellow bar), and the yellow dotted line marks the anterior-posterior boundary. Yellow arrowheads mark some trichomes which emerge from posterior cell edges, rather than from distal cell edges as normally. Scale bar 10 μm.