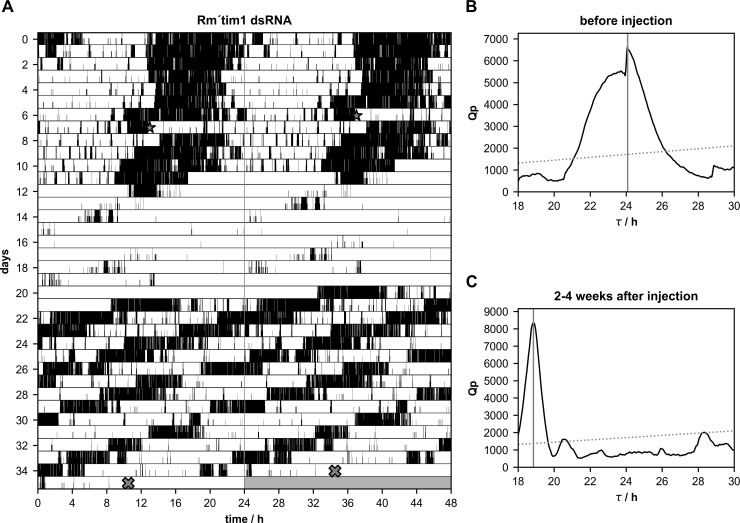
Fig 5.
A-C. Injections of Rm´tim1 dsRNA significantly shortened the free-running period(τ) of circadian locomotor activity rhythms (n = 8 of 10; p = 0.0016). (A) Double-plotted running wheel activity of a Madeira cockroach in constant darkness. Rm´tim1 dsRNA was injected at day 7 (star) of the recording. The injected cockroach retained synchronized circadian locomotor activity rhythms, but with a significantly shortened period. At day 35 of the locomotor activity recording the cockroach was sacrificed (cross) and qPCR was used to confirm the knockdown. Chi-square periodogram analysis of the activity shown in (A), 1–7 days before dsRNA injection revealed a period of 24.08 h (B) and a period of 18.85 h 2–4 weeks after the injection (C).