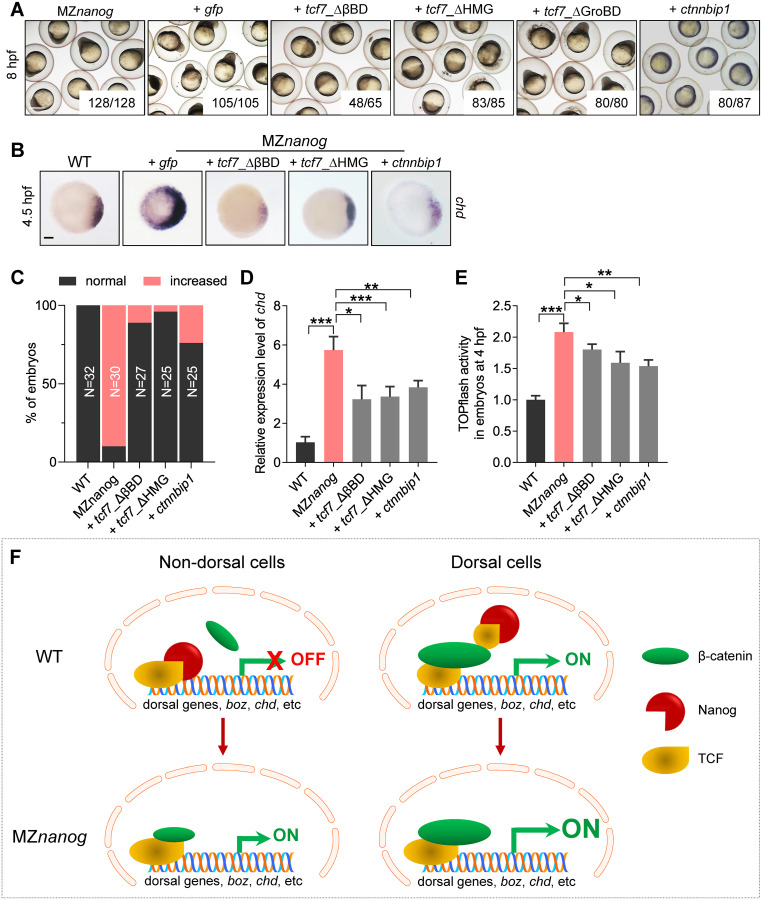
Fig 8. Confrontation of the β-catenin transcriptional activity in nucleus rescues the developmental defect of MZnanog.
(A) Injection of tcf7)_ΔβBD, tcf7_ΔHMG, or ctnnbip1 mRNA rescued the early developmental defects of MZnanog, whereas overexpression of tcf7_ΔGroBD did not. Phenotypes were observed at 8 hpf. At least 50 embryos were injected, and 3 independent experiments were performed. The numbers below the morphology pictures mean number of embryos showing representative phenotype/total number of embryos. Scale bar, 500 μm. (B) WISH analysis showing excessive and ectopic expression of chd in MZnanog was rescued by overexpression of tcf7)_ΔβBD, tcf7_ΔHMG, or ctnnbip1 at 4.5 hpf. Scale bar, 100 μm. (C) Statistical analysis of the embryos in panel B. N represents analyzed embryo number. (D) Relative mRNA level of chd in embryos of WT, MZnanog, and MZnanog injected with tcf7)_ΔβBD, tcf7_ΔHMG, or ctnnbip1 mRNA at 4.5 hpf examined by RT-qPCR. Error bars, mean ± SD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (E) Relative β-catenin transcriptional activity in embryos of WT, MZnanog, and MZnanog injected with tcf7)_ΔβBD, tcf7_ΔHMG, or ctnnbip1 mRNA at 4 hpf examined by TOPflash assay. Error bars, mean ± SD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (F) The model of Nanog repressing β-catenin transcriptional activity in nondorsal cell nuclei in WT embryo, and the ectopic activation of β-catenin transcriptional activity in the absence of Nanog in MZnanog embryo. In nondorsal cells of WT embryo, the amount of nucleus-deposited maternal Nanog (red cartoon object) is much higher than that of the nuclear β-catenin (green cartoon object); therefore Nanog binds to TCF (yellow cartoon object), and the β-catenin transcriptional activity is not activated. In nondorsal cells of MZnanog embryo, however, because of the absence of nanog in the nuclei, the small amount of nuclear β-catenin binds to TCF to activate the expression of dorsal genes (boz, chd, etc.), resulting in hyperdorsalization of the embryo. In dorsal cells of WT embryo, the amount of nuclear β-catenin is much higher than Nanog and facilitates the formation of β-catenin-TCF transcriptional complex to induce the expression of dorsal genes, boz, chd, etc. The P values in this figure were calculated by Student t test. The underlying data in this figure can be found in S1 Data. hpf, hours post fertilization; MZnanog, maternal zygotic mutant of nanog; RT-qPCR, reverse-transcription quantitative PCR; tcf7)_ΔβBD, β-catenin-binding domain deleted Tcf7, tcf7_ΔHMG, high mobility group (LEF1-binding domain) deleted Tcf7; tcf7_ΔGroBD, Groucho-binding domain deleted Tcf7; WISH, whole-mount in situ hybridization; WT, wild type.