Fig. 1.
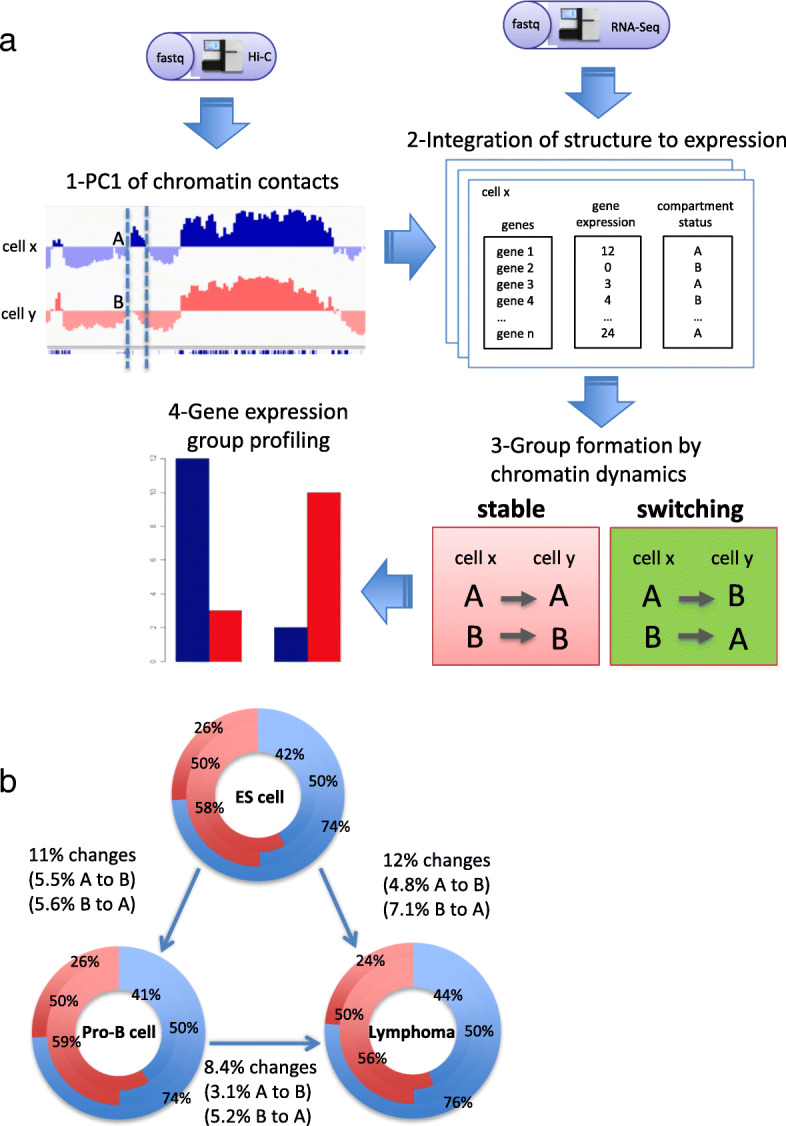
a Representation of our integrative analysis. First, we obtained the first principal component (PC1) values from Hi-C chromatin maps and assigned each gene to active (A compartment) or inactive (B compartment) in each cell. Next, we included gene expression levels to the matrix profiles. Compartment classification of each gene in two cell types categorized four compartment switch groups (i.e., stable A, A to B, B to A, and stable B). Stable regions have the same compartments in two different cells. Finally, we obtained the overall gene expression levels on the groups. b Chromatin organization characterization at compartment level in ES cells, pro-B cells, and Lymphoma. Each graph represents the compartment landscape; blue is for A and red is for B. The inner layer represents the percentage of genomic sequences within A or B compartments; middle layer represents the ratio of A and B compartments; outer layer represents the percentage of genes contained in each compartment
