Figure 1.
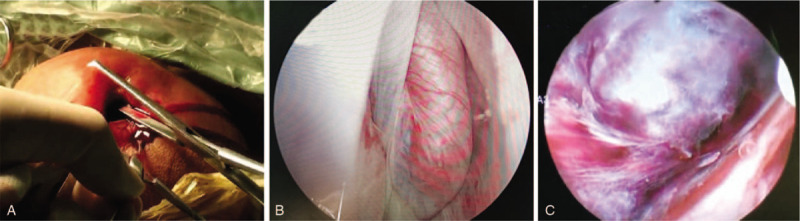
Key signs of scrotoscopy in diagnosing TT. A: When reaching into the cavity of perididymis, a slight dark red, non-coagulable fluid flows out, which is the first typical performance of TT under scrotoscopy, usually indicating testicular necrosis. B: TT is in a position of horizontal plane, and a spiral spermatic cord is observed, the second typical but the most important performance of TT under scrotoscopy. C: Under the scrotoscope, the testis and epididymis appear dark black, also a sign of different degrees of testicular necrosis. TT = testicular torsion.
