FIGURE 6.
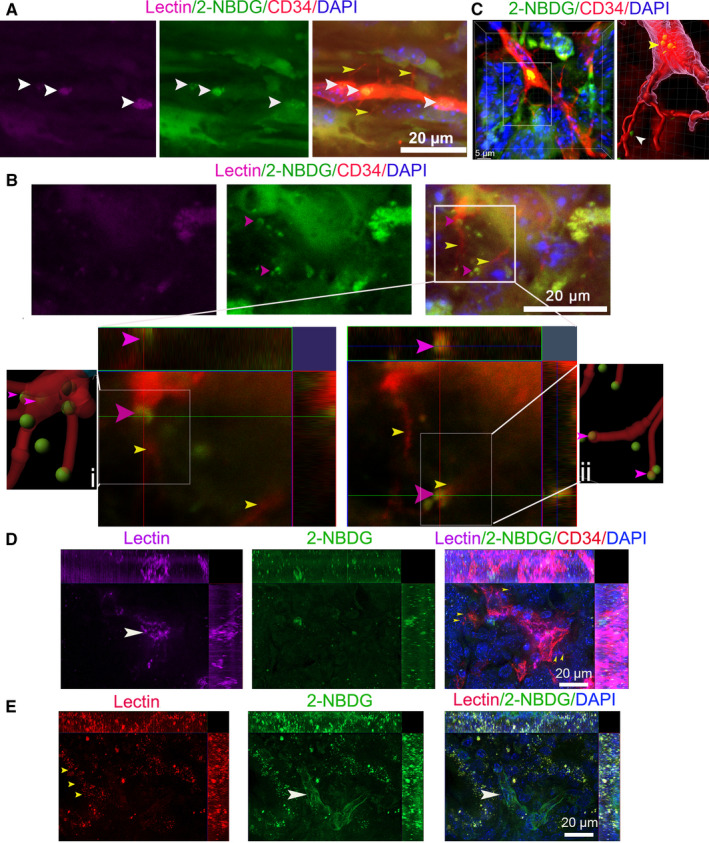
Perfused staining results with lectin do not reflect the nutrient trafficking in PCs. (A0 PC images in KIC mice coperfused with Lectin‐Alexa 633 and 2‐NBDG were stained by CD34 antibody (yellow arrows, basal microvilli; white arrows, 2‐NBDG). (B) Images of 2‐NBDG distribution in the basal microvilli microvasculature of KIC mice coperfused with Lectin‐Alexa 633 and 2‐NBDG. The two images in lower panels show magnification of the boxed region in the upper panel (at different Z‐layers). IMARIS spots and filament analyses showed that 2‐NBDG exists in basal microvilli or binds with basal microvilli (pink arrows, 2‐NBDG‐containing vesicle‐like structure; yellow arrows, basal microvilli). (C) A typical 2‐NBDG vesicle‐like structure present at the base of the basal microvilli in the microvasculature lumen of KC mice coperfused with Lectin‐Alexa 633 and 2‐NBDG and stained by CD34 antibody Right panel is the image processed by Imaris 9.5 (yellow arrow, basal 2‐NBDG vesicle‐like structure; white arrow, 2‐NBDG in basal microvilli). (D) Images of CD34 antibody immunostaining in the PC of a KPIC mouse coperfused with 2‐NBDG and Lectin‐Alexa 633 showed that Lectin‐Alexa 633 partially labeled the microvasculature of basal microvilli (white arrow, microvessel; yellow arrows, basal microvilli). (E) Images of the PC in KPIC mice co‐perfused with 2‐NBDG and Lectin‐Alexa 633 show that the microvessels are poorly labeled by Lectin‐Alexa 633 but contain decent levels of 2‐NBDG (white arrow, microvessels; pink arrows, tumor cells; yellow arrows, lectin dots in neoplastic cells)
