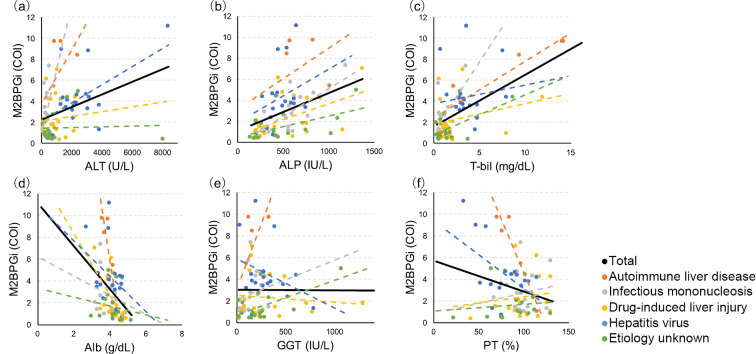
Figure 2.
Correlations between the serum level of M2BPGi and serum levels of ALT, ALP, T-bil, Alb, and GGT, as well as the serum PT activity. Black line, correlations for the overall study population; dotted lines, correlations according to the etiology. The serum M2BPGi level was significantly correlated with the serum ALT level in the overall study population (r=0.34, p<0.01), and this correlation differed according to etiology (a). The serum M2BPGi level was significantly correlated with the serum levels of ALP (r=0.46, p<0.0001), T-bil (r=0.49, p<0.0001), and Alb (r=-0.45, p<0.0001) in the overall study population and in each etiology group (b, c, d). The serum M2BPGi level was not correlated with the serum GGT level or PT activity in the overall study population, and the correlations differed according to the etiology of acute liver injury (e, f). Orange dotted line, autoimmune liver disease; gray dotted line, infectious mononucleosis; yellow dotted line, drug-induced liver injury (DILI); blue dotted line, hepatitis virus (hepatitis A virus/hepatitis B virus); green dotted line, etiology unknown. M2BPGi: Mac-2-binding protein glycosylation isomer, ALT: alanine aminotransferase, ALP: alkaline phosphatase, T-bil: total bilirubin, Alb: albumin, GGT: γ-glutamyltransferase, PT: prothrombin time