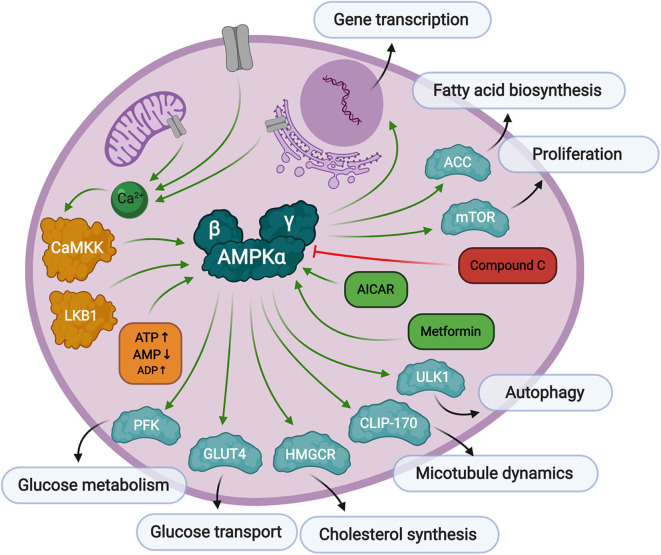
Figure 2.
Overview of AMPK signaling. AMPK responds to low levels of ATP in the cell. First, AMP binds to the AMPKγ regulatory subunit causing a conformational change exposing threonine-172 in the AMPKα catalytic subunit. Then, Thr-172 is phosphorylated by upstream kinases, CaMKK, or LKB1, fully activating AMPK kinase activity toward substrates responsible for preserving cellular energy. AMPK can be activated by AICAR or metformin treatment, and inhibited by Compound C.