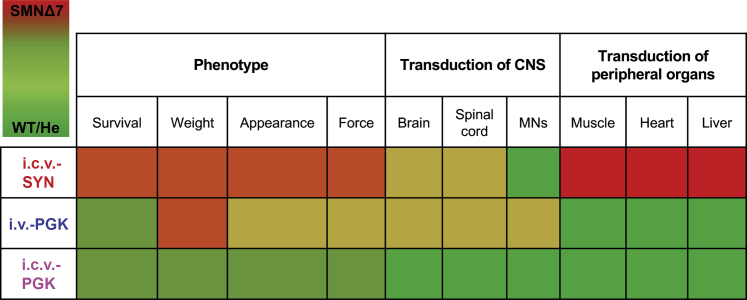
Figure 8.
Graphical Summary of the Main Findings of the Study
The effects of each treatment (i.c.v.-SYN, i.v.-PGK, and i.c.v.-PGK) on the phenotype (survival, body weight, general appearance, and neuromuscular functions) are classified according to a color code, in which brilliant red and brilliant green correspond to SMNΔ7 and WT/He mice, respectively. The effects on the phenotype are compared to transduction of CNS (brain, spinal cord, and MNs) and peripheral organs (skeletal muscle, heart, and liver). SMN expression restricted to neurons (i.c.v.-SYN) mediates a modest improvement of the SMNΔ7 mouse phenotype. SMN expression in the peripheral organs contributes to a better rescue of the phenotype (i.v.-PGK and i.c.v.-PGK). High expression of SMN in both CNS tissues and peripheral organs results in the best rescue of SMA mice (i.c.v.-PGK), which are still not comparable to WT or He mice. This work highlights the importance of SMN expression in the CNS and peripheral organs for complete rescue of the SMNΔ7 phenotype.