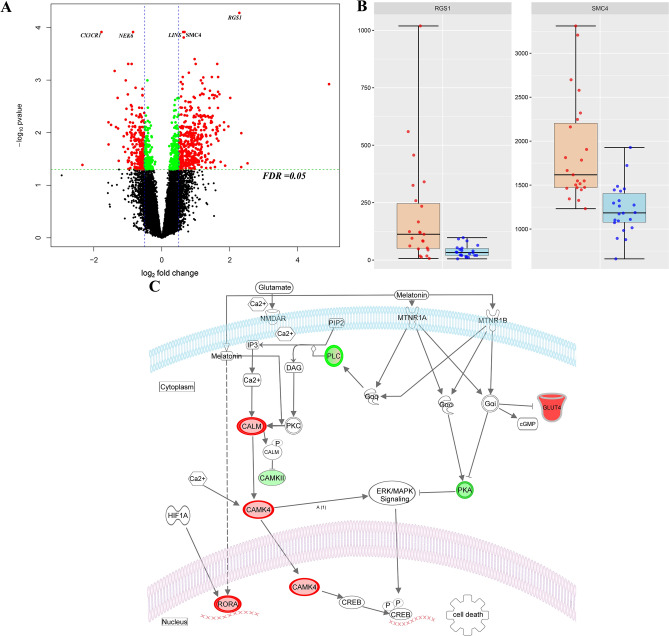
Figure 1.
(A) Volcano plot showing the significant genes identified in the comparison of neonates with adverse versus good outcome, plotted according to log2 fold-change (x axis) and log10 p value (y axis). In green are genes with false discovery rate (FDR) < 0.05 and log2 fold change < 0.4 in red are genes with FDR < 0.05 and log2 fold change > 0.4. (B) Box plot (median, IQR) of gene count values expressed as Fragments Per Kilobase of transcript per Million mapped reads (FPKM) (y axis) of the 6 most significant genes for children with normal (blue) compared with abnormal neurodevelopmental outcome at 2 years (orange). (C) Brain hypoxia leads to Ca2+ influx with activation of the Ca2+/calmodulin dependent protein kinase IV (CaMK-IV) cascade. CaMK-IV in the cytosol has a proapoptotic effect and is responsible for hypoxic neural cell death both through activation of MAP kinases signalling in the cytosol and through phosphorylation of cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) in the nucleus, which enhances the expression of pro-apoptotic proteins. Melatonin binds to its plasma membrane receptor MTNR1, to calmodulin and to nuclear receptor retinoid-related receptor alpha (RORA) increasing its expression. RORA is also considered a downstream target of HIF-1α and its levels have been found upregulated in the cellular response to hypoxia. MTNR1A and MTNR1B activation increases PKC activity through activation of Gαq, which stimulates the PLC signalling cascade and leads to inhibition of Ca2+/calmodulin dependent protein kinase (CAMK). Both MTNR1A and MTNR1B activation by melatonin inhibits cAMP formation. Furthermore, activation of MTNR1B decreases the expression of the glucose transporter GLUT4, which in turn decreases glucose uptake. The upregulated genes in our analysis are shown in red, while the downregulated genes are shown in green. CALM Calmodulin, CAMK4 calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase 4, CAMKII calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II, CREB cAMP-response element binding protein, DAG diacylglycerol, ERK extracellularly regulated kinase, Gαq Gq protein alpha subunit, Gαi α subunit of the heterotrimeric G protein complex, GLUT4 Glucose transporter type 4, Hif-1 alpha Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha, PIP2 Phosphatidylinositol biphosphate, PKA protein kinase A, PKC Protein Kinase C signalling, MAPK mitogen-activated protein kinases, MTNR1A Melatonin receptor type 1A, MTNR1B Melatonin receptor type 1B, IP3 Inositol trisphosphate, NMDAR N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor, RORA Retinoid-related receptor alpha. A,B were created using R (version 4.0.0) (https://cran.r-project.org/). C Was created through the use of Ingenuity pathway software (QIAGEN Inc., https://www.qiagenbioinformatics.com/products/ingenuity-pathway-analysis).