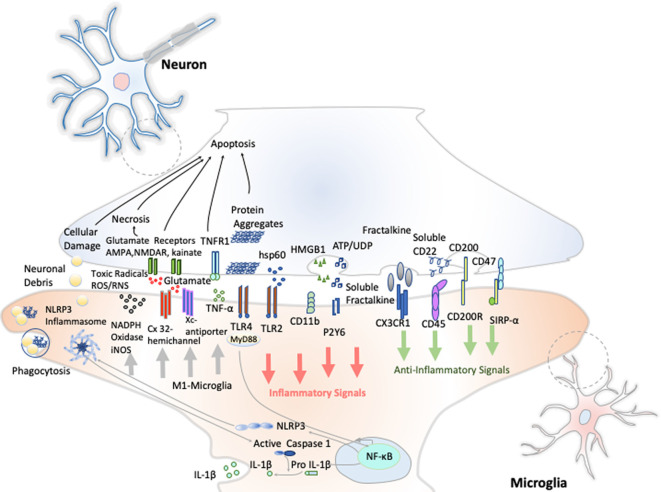
Figure 2.
Neuron–microglia crosstalk. An amplification of neuron–microglia interactions is shown in green arrow signals. Homeostatic neurons actively produce anti-inflammatory signals aimed at inhibiting the acquisition of the inflammatory M1-like phenotype by microglial cells. During neurodegenerative disorders or after nervous system injury, cellular mediators associated with damage are activated (salmon arrows) triggering the M1 microglia state that releases reactive species of oxygen and nitrogen (ROS and RNS), glutamate and TNF-α (gray arrows) Importantly, an oxidative environment favors further oxidation and self-aggregation of proteins in damaged neurons, which promotes neuronal death that subsequently stimulates TLRs and the NLRP3 inflammasome in microglia enhancing the production of IL-1β.