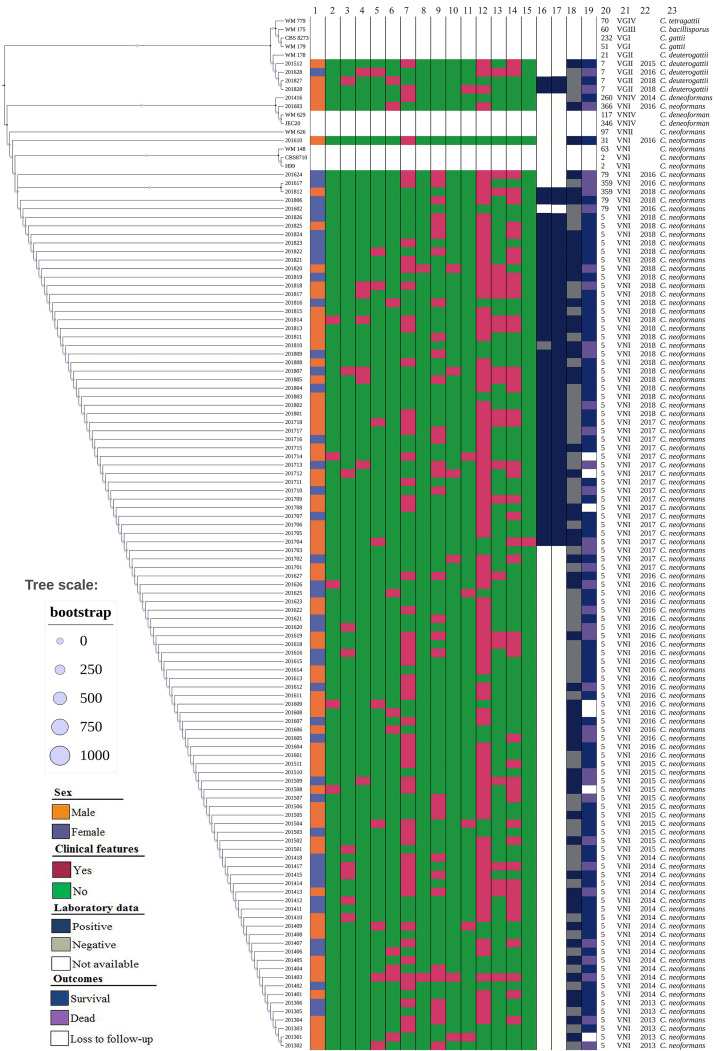
FIGURE 3.
The phylogenetic tree diagram of 110 clinical unique strains of Cryptococcus and various type strains based on MLST sequences: C. neoformans s.s. (105 strains) and C. deneoformans (1 strain), and C. deuterogattii (4 strains) clustered into different groups. Reference sequences of VNI, VNII, VNIII, VNIV, and VGII as outgroups are included. From left to right: 1 Sex; 2–15, clinical features: 2 Speech difficulties; 3 Visual disturbance; 4 Brinell sign; 5 Altered mental status; 6 Dizziness; 7 Fever/chill; 8 Hemiplegia; 9 Nausea/vomiting; 10 Palsies; 11 Unstable walking; 12 Headache; 13 Klinefelter sign; 14 Nick stiffness; 15 Sepsis shock; 16∼18 Laboratory data:16 CSF cryptococcal antigen; 17 Blood cryptococcal antigen; 18 India ink staining; 19 Outcomes; 20 Sequence type (ST); 21 Molecular type; 22 Year of isolation of Cryptococcus strains; 23 Cryptococcus species.