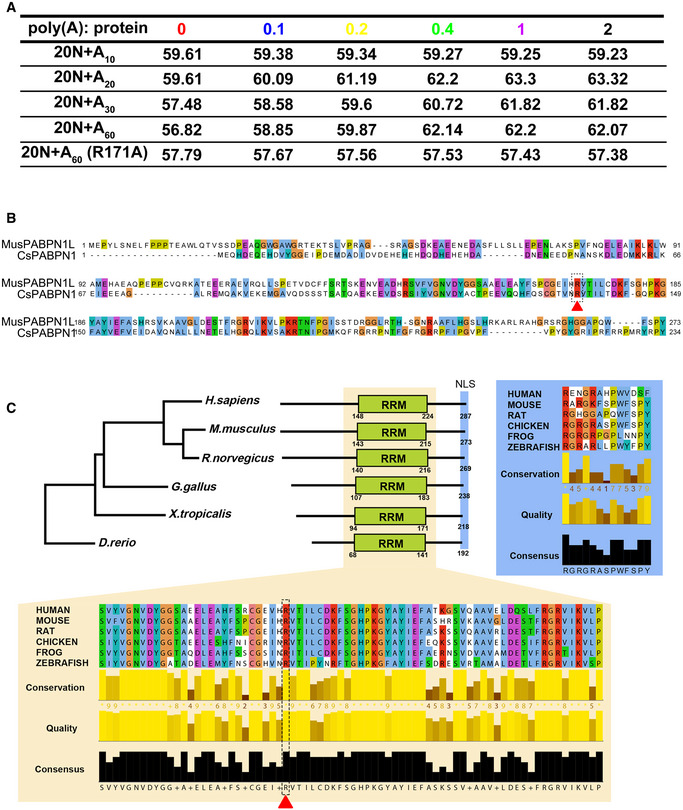
Sequence alignment and a phylogenetic tree analysis of PABPN1L. PABPN1L aminol acid sequences from
H. sapiens (
A6NDY0),
M. musculus (
Q5XFR0),
R. norvegicus (
B0BNE4),
G. gallus (F1NWW9),
X. tropicalis (
Q28GL9), and
D. rerio (E9QGY6) were analyzed by Clustal Omega Multiple Sequence Alignment algorithm (
https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/). The phylogenetic tree was plotted based on results from sequence alignments using the neighbor‐joining tree algorithm without distance corrections. Sequence alignments and quality parameters of RNA recognition motif (RRM, highlighted in light yellow) and nucleus localization signal (NLS, highlighted in light blue) were generated by Jalview (
http://www.jalview.org/). The broken circle and arrowhead indicate Arg‐171 of mouse PABPN1L.