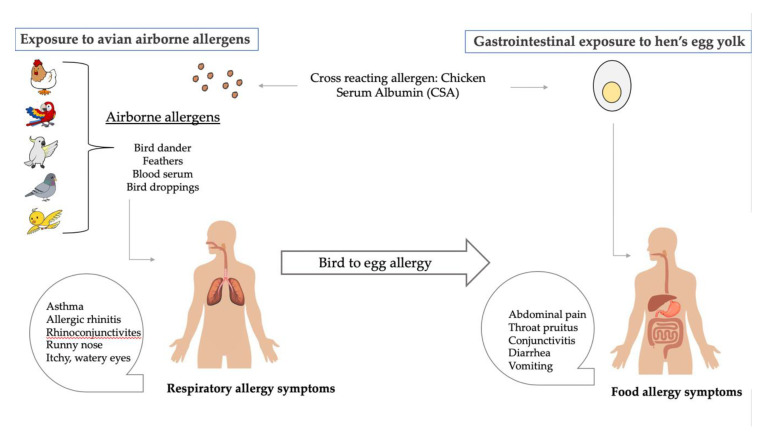
Figure 2.
An illustration of the bird-egg syndrome. An individual develops an allergy to hen’s egg yolk following exposure to birds. Sensitisation to inhalant avian allergens occurs, resulting in respiratory allergy symptoms. The cross-reactive allergen that is responsible for producing both respiratory and gastrointestinal allergy symptoms in bird-egg syndrome is identified as Gal d 5 (α-livetin/chicken serum albumin), a type of serum albumin present in birds and the egg yolk as well (figure adapted from Dhanapala et al. [34]).