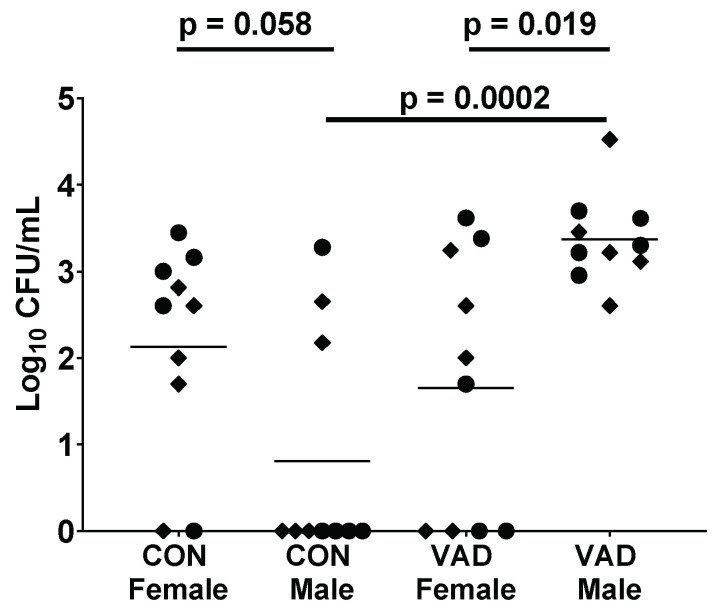
Figure 1.
Vitamin A deficient (VAD) male mice exhibit higher bacteria burdens than control males and VAD females. To produce VAD mice, pregnant C57BL/6 (H2-b) mice were purchased from Jackson Laboratories (Bar harbor, ME). Mice were placed on either a control or a VAD diet upon their arrival in the animal facility at St. Jude (days 4–5 gestation). VAD (cat. no. 5WA2, Test Diets) and control (cat. no. 5W9M) diets differed only in vitamin A content, containing either 0 or 15 international units (IU)/g vitamin A palmitate, respectively. Upon reaching adulthood, C57BL/6 control (CON) and VAD mice were lightly anesthetized with isoflurane and intranasally infected with 0.5–1 × 105 CFU of Streptococcus pneumoniae, strain A66.1 (as described previously [86,98,99]). Lung bacterial titers were determined 24 h post-infection, assigned the value ‘1′ if below detection. Each dot represents an individual mouse. Results from two experiments are shown, respectively, indicated by circles and diamonds. Significant differences between the paired groups were determined by Mann–Whitney U tests.