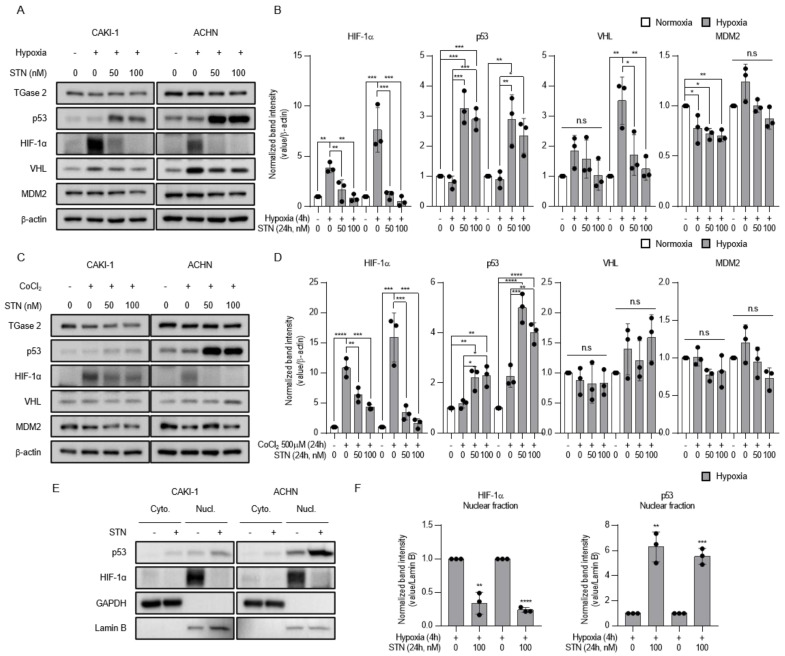
Figure 2.
TGase 2 inhibition induces p53-dependent inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α in hypoxia. (A) Cells were treated with STN (streptonigrin, TGase 2 inhibitor) for 24 h and incubated for 4h in hypoxia (1% O2). (B) The image J analysis of Western blotting of Figure 2A. (C) Cells were treated with STN and CoCl2 (cobalt chloride, 500 μM) and incubated for 24 h in normoxia. Whole cell lysates were subjected to the immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. β-actin was used as a loading control. (D) The image J analysis of Western blotting of Figure 2C. (E) Cells were treated with or without STN (100 nM) for 24 h and incubated for 4 h in hypoxia (1% O2). GAPDH was used as a cytosolic fraction loading control and Lamin B was used as a nuclear fraction loading control. (F) The image J analysis of Western blotting of Figure 2E. Densitometry of proteins in nuclear fraction is used to normalize the Lamin B. Error bar represents SD. GraphPad Prism software used to perform one-way ANOVA or t-test, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001. ns = not significant. Data are representative of three independent experiments.