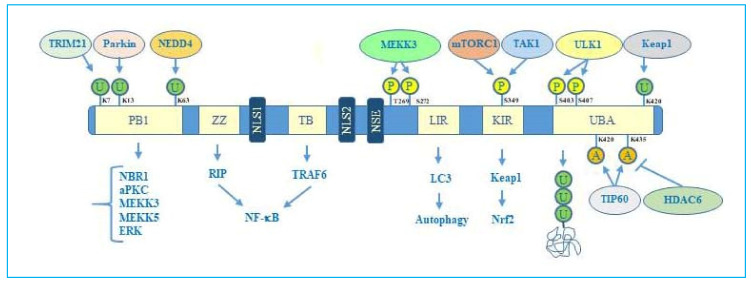
Figure 1.
p62 structure, functional domains, post-translational modifications, and interactors. In particular, the figure shows Phox/Bem1p (PB1) domain, which is important for p62 oligomerization, with indicated ubiquitination sites, relative ubiquitinating enzymes (Trim21, parkin, NEDD4) and interactors (NBR1, atypical protein kinase C (aPKC), MEKK3, MEKK5, ERK); Zinc finger ZZ and TRAF bindingTB domains necessary for interaction with receptor interacting protein (RIP) and TRAF6, respectively, to activate NF-κB signalling; nuclear localization sequences (NLS1 and NLS2), and nuclear export sequence (NES) which account for nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling of p62; LYR and Keap1-interacting region (KIR) domains that interact with LC3 and Keap1 respectively to promote selective autophagy and nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2)-mediated signalling. Ubiquitin associated (UBA) domain is fundamental for recognition of poly-ubiquitinated cargo during selective autophagy. Post-translational modification sites including phosphorylation, acetylation, and ubiquitination together with the respective regulative enzymes (MEKK3, mTORC1, TAK1, Keap1, Tip60, HDAC6) are also indicated.