Table 1.
Structures, binding type and bioactivities of Δ9-THC, CBD, Δ9-THCP and CBDP.
| Phytocannabinoids | Binding Type/CB | Ki (nM)/CB | EC50/IC50 (nM)/CB | Bioactivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
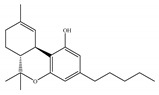 (a) Δ9-THC |
Partial agonist/CB1, CB2 | 5.00~80.0/CB1 1.70~75.0/CB2 [14] |
13.0~87.0/CB1 41.8, 61.0/CB2 [14] |
Analgesic, antiemetic, orexigenic [53]; relief from muscle spasms/spasticity in multiple sclerosis [61] |
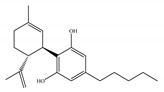 (b) CBD |
Antagonist/inverse agonist, negative allosteric modulator/CB1 Partial agonist/CB2 |
73.0~>10,000/CB1 370~>10,000/CB2 [14] |
3860/CB1 503, 2270/CB2 [14] |
Anti-inflammatory, anti-nociceptive, anti-oxidant, anti-ischemic, neuroprotective, immunosuppressive [62]; anxiolytic [43,62] |
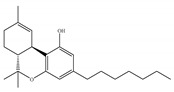 (c) Δ9-THCP |
Agonist/CB1, CB2 | 1.20/CB1 6.20/CB2 [39] |
NA | Analgesic [39] |
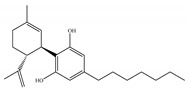 (d) CBDP |
NA | NA | NA | NA |
Ki: binding constant; EC50: half-maximal effective concentration; IC50: half-maximal inhibitory concentration; NA: not available.
