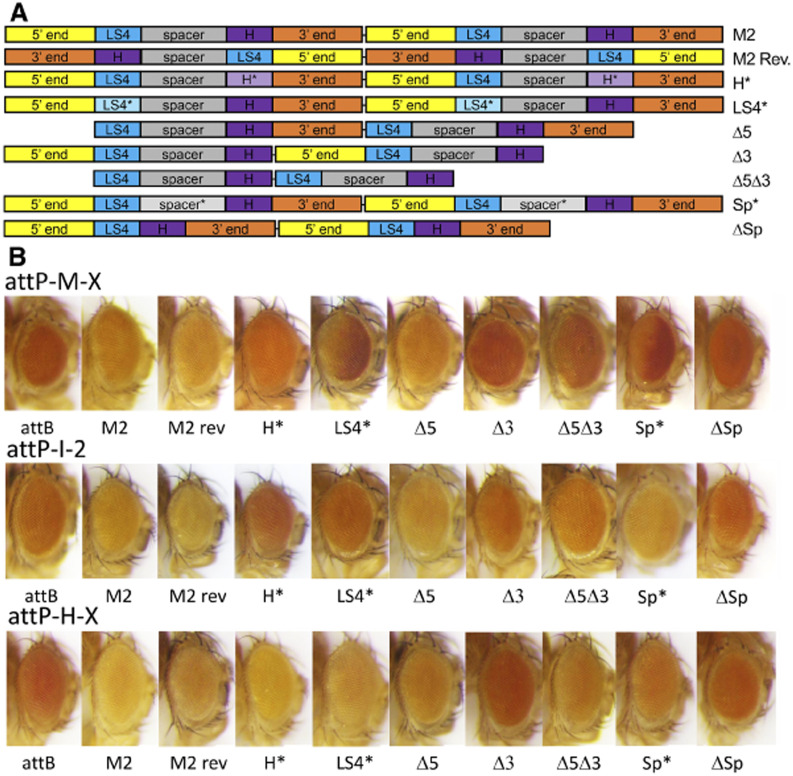
Figure 2.
CPE analysis of M fragment derivatives. (A) Schematics of the dimeric insulator constructs tested. The M fragment was divided into the 5′ end, 3′ end, the LS4 sequence, the H (high affinity BEAF binding site) sequence, and spacer sequence between LS4 and H. Sequences were deleted or mutated as indicated. Mutant sequences are denoted by a * and lighter rectangle shading. Dimers were placed between an attB site and the 5′ end of mini-w for integration into chromosomal attP sites. As in Figure 1A, there is an scs insulator downstream of mini-w. (B) Eye color of 2–3 day old heterozygous transgenic female flies with the indicated 5′ insulator sequences. Release 6 locations of the attP sites are: attP-M-X: chrX:10,366,253; attP-I-2: chr2:7,040,089; attP-H-X: chrX:13,128,844. attB: no 5′ insulator. Results show that 5′ end and spacer sequences are dispensable, while the 3′ end, LS4, H and spacing between LS4 and H play a role in insulator function.