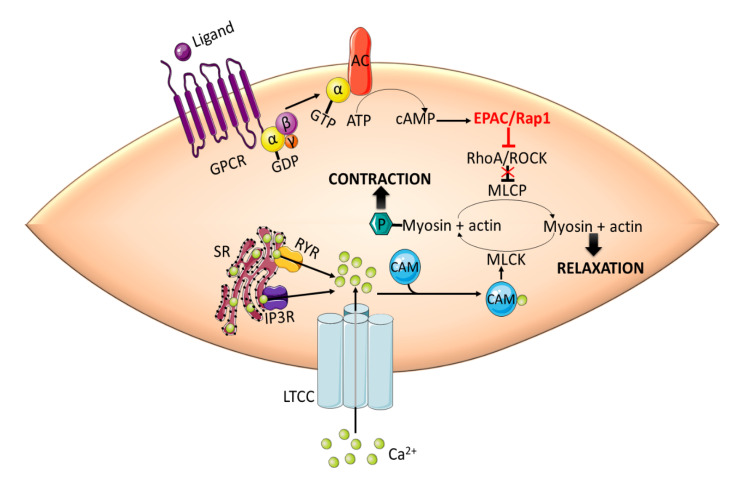
Figure 2.
EPAC promotes vasorelaxation in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) by inhibiting RhoA/ROCK signaling. Activation of RhoA/ROCK phosphorylates MLCP and inhibits its phosphatase activity. This in turn increases the phosphorylation of MLC by MLCK, which is activated by Ca2+-CaM complex, and induces contraction. cAMP-mediated activation of EPAC/Rap1 releases the inhibitory effect of RhoA/ROCK on MLCP leading to the dephosphorylation of MLC and subsequent relaxation. CaM: calmodulin; GPCR: G-protein coupled receptor; IP3R: inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor; LTCC: L-type calcium channel; MLC: myosin light chain; MLCK: myosin light chain kinase; RYR: ryanodine receptor; SR: sarcoplasmic reticulum.