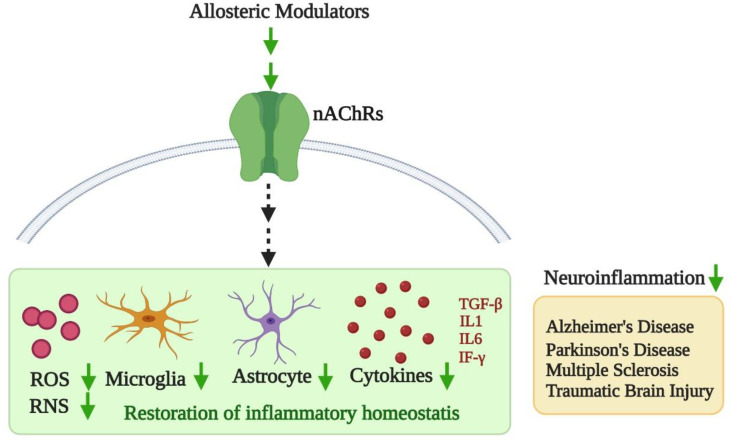
Figure 1.
Proposed model of allosteric modulation in inflammation: Allosteric modulators can potentially restore cholinergic transmission in the cells by binding to neuronal acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs). This can attenuate the exacerbated expression of predominant inflammatory mediators such as reactive oxygen species (ROS), reactive nitric oxide species (RNS), astrocytes, microglia and cytokines such as TGF-β (Transforming growth factor-beta), interleukin 1 (IL-1), interleukin 6 (IL-6) and interferon-gamma (IF-γ).