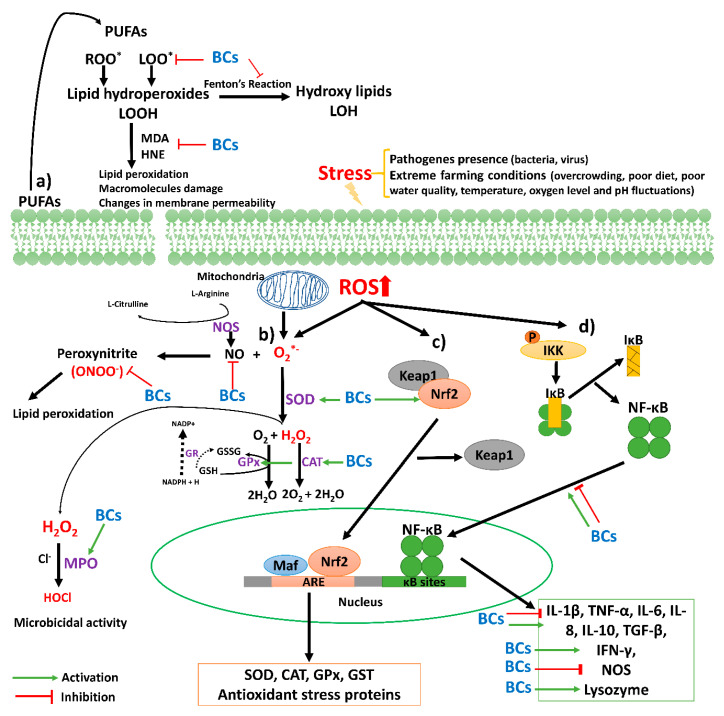
Figure 2.
Graphical representation of the mechanism of action of bioactive compounds on the antioxidant and immune response. (a) Lipid peroxidation chain reaction, (b) antioxidant enzymes reaction, (c) Nrf2 pathway associated to the antioxidant response, and (d) NF-κB pathway associated to the immune response. Abbreviations: ARE—antioxidant response element; BCs—bioactive compounds; CAT—catalase; GPx—glutathione peroxidase; GR—glutathione reductase; GSH—glutathione; GSSG—oxidized glutathione; GST—glutathione transferase; HNE—4-hydroxynonenal; HOCl—hypochlorous acid; IFN-γ—interferon-gamma; IkB—inhibitor protein of nuclear factor kappa-light chain-enhancer of activated B cells; IKK—kinase complex; IL—interleukin; Keap1—Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; LOO*—lipid hydroperoxyl radical; Maf—musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma; MDA—malondialdehyde; MPO—myeloperoxidase; NADP+—nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NADPH—reduced form of NADP; NF-κB—nuclear factor kappa-light chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NOS—nitric oxide synthase; Nrf2—NF-E2-related factor 2; PUFAs—polyunsaturated fatty acids; ROO*—peroxyl radical; SOD—superoxide dismutase; TGF-β—transforming growth factor-beta; TNF-α—tumor necrosis factor-alpha.