FIGURE 1.
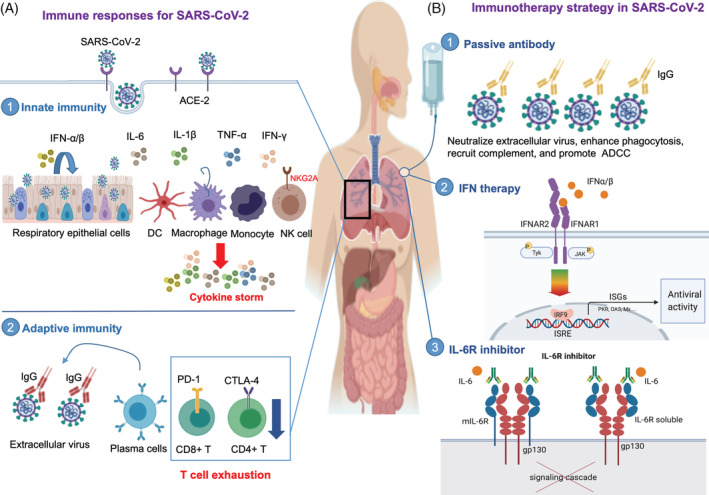
Immune responses and immunotherapy strategy in SARS‐CoV‐2 infection. Immune response to SARS‐CoV‐2 involving innate and adaptive immunity. A1, SARS‐CoV‐2 enters the host cells by binding the receptor for angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). The infected cells then release interferon type I (IFN‐α/β); innate immune cells respond to the IFNs by establishing an antiviral state. In case of severe infection, the viruses are sensed by monocytes, tissue macrophages, and resident dendritic cells resulting in uncontrolled proinflammatory cytokine (IFN, TNF‐α, IL‐1β, and IL‐6) production, leading to a phenomenon called the cytokine storm, which damages the host’s respiratory epithelial cells. Exhausted natural killer cells with increased expression of the inhibitory receptor, NKG2A, are also seen in SARS‐CoV‐2. A2, In SARS‐CoV‐2 infection, increased antibody production and poor T cell responses are observed (A2). CD4+ T cell and CD8+ T cell numbers decrease, and the exhausted phenotype, which is characterized by a higher expression of inhibitory receptors, such programmed death receptor‐1 (PD‐1) and cytotoxic T lymphocyte associated antigen‐4 (CTLA‐4), is seen. Immunotherapy strategies for SARS‐CoV‐2 have been proposed. B1, Transferring convalescent sera with neutralizing antibodies from the recovered patients. The antibodies can directly bind to SARS‐CoV‐2 and prevent the virus from infecting new cells (neutralization), enhance phagocytosis (opsonization), recruit complement to lyse infected cells or neutralize the viruses, and promote NK cell mediated killing of infected cells through antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). B2, IFN α/β bind to IFN receptors and induce an antiviral response by expressing several interferon stimulated genes (ISGs), such as PKR, OAS, and Mx. The protein product of ISGs controls viral infection. (B3) The IL‐6R inhibitor (such as tocilizumab) binds to the membrane bound IL‐6 receptor (mIL‐6R) and soluble IL‐6 receptor (soluble IL‐6R). Binding of tocilizumab to IL‐6R inhibits the IL‐6 signaling pathway
