Figure 1.
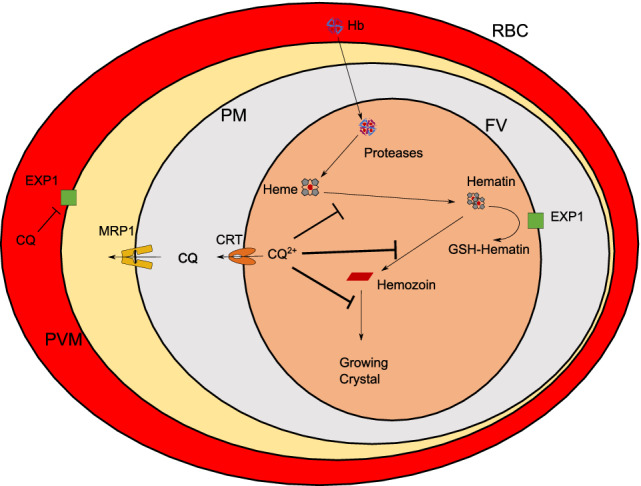
Suggested modes of action of chloroquine against Plasmodium falciparum parasites. Chloroquine can (1) prevent the formation of hemozoin by masking functional groups of hematin and the growing hemozoin crystal resulting in accumulation in the food vacuole (FV) as CQ2+ and (2) inhibit the activity of PfEXP1 which is involved in reduced glutathione (GSH)‐mediated detoxification of heme. CQ resistance in P. falciparum parasites is believed to be inferred by mutations in PfCRT and PfMRP1 transporters that promote efflux of CQ out of the FV and the parasite, respectively. RBC, red blood cell; PVM, parasitophorous vacuole membrane; PM, parasite membrane; FV, food vacuole; CQ, chloroquine; CQ2+, protonated chloroquine as present in the FV; Hb, hemoglobin; EXP1, Plasmodium falciparum exported protein 1 (a glutathione‐S‐transferase); CRT, Plasmodium falciparum CQ resistance transporter; MRP1, Plasmodium falciparum multidrug resistance‐associated protein 1. [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
