Figure 2.
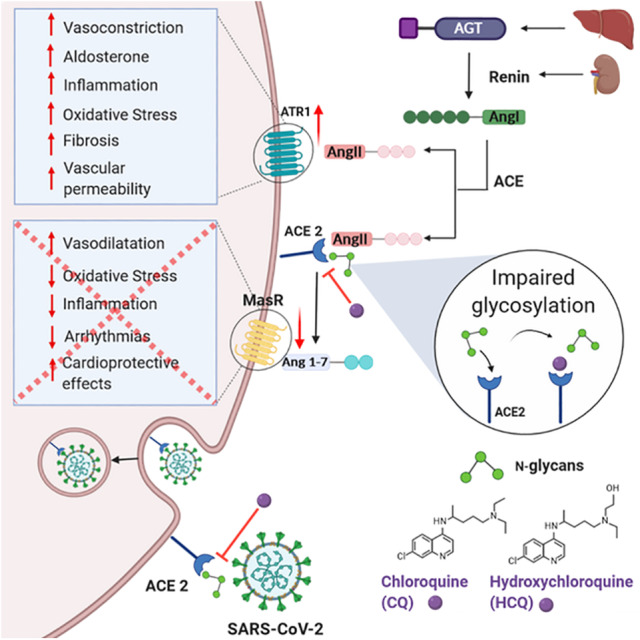
Interference of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine in the renin‐angiotensin system (RAS). Angiotensinogen, produced in the liver, is cleaved by the renin protease produced in the kidney. Cleavage of Ang I by ACE produces the active octapeptide Ang II that acts via the AT1R, inducing vasoconstriction, production of aldosterone, increased inflammation, oxidative stress, fibrosis, and vascular permeability. Ang II levels are regulated by ACE2 that cleaves Ang II and produces Ang 1–7, a heptapeptide that acts via the Mas receptor, inducing vasodilatation and cardioprotective effects, while decreasing oxidative stress, inflammation and arrhythmias. Expression of ACE2, the SARS‐CoV‐2 cell receptor, is decreased by the endocytosis process that allows viral entry. CQ and HCQ inhibit viral entry by impairing terminal glycosylation of ACE2, which may reduce enzyme activity, elevating Ang II concentration and favoring the pressor axis. CQ, chloroquine; HCQ, hydroxychloroquine; AGT, angiotensinogen; Ang I, angiotensin I; Ang II, angiotensin II; ACE, angiotensin‐converting enzyme; ACE2, angiotensin‐converting enzyme 2; AT1R, Ang II receptor type 1; MasR, Mas receptor. [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
