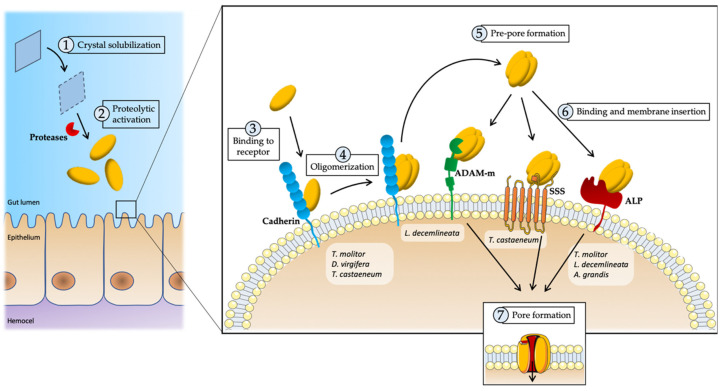
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of the particularities in the mechanism of action of crystal proteins against coleopteran pests. (1) Crystal solubilizes in the acidic conditions of the coleopteran midgut lumen and (2) activates into toxin by proteolytic processing of the protoxin by the specific digestive enzymes, specially cysteine and aspartic proteases. (3) Toxins are able to bind to a first receptor (CADR), (4) oligomerizate and (5) form an oligomeric pre-pore structure that (6) is able to bind to a second specific receptor (ADAM metalloproteases/GPI-anchored alkaline phosphatases/sodium solute symporters). This event induces the insertion into the membrane, leading to (7) pore formation and finally to cell lysis.