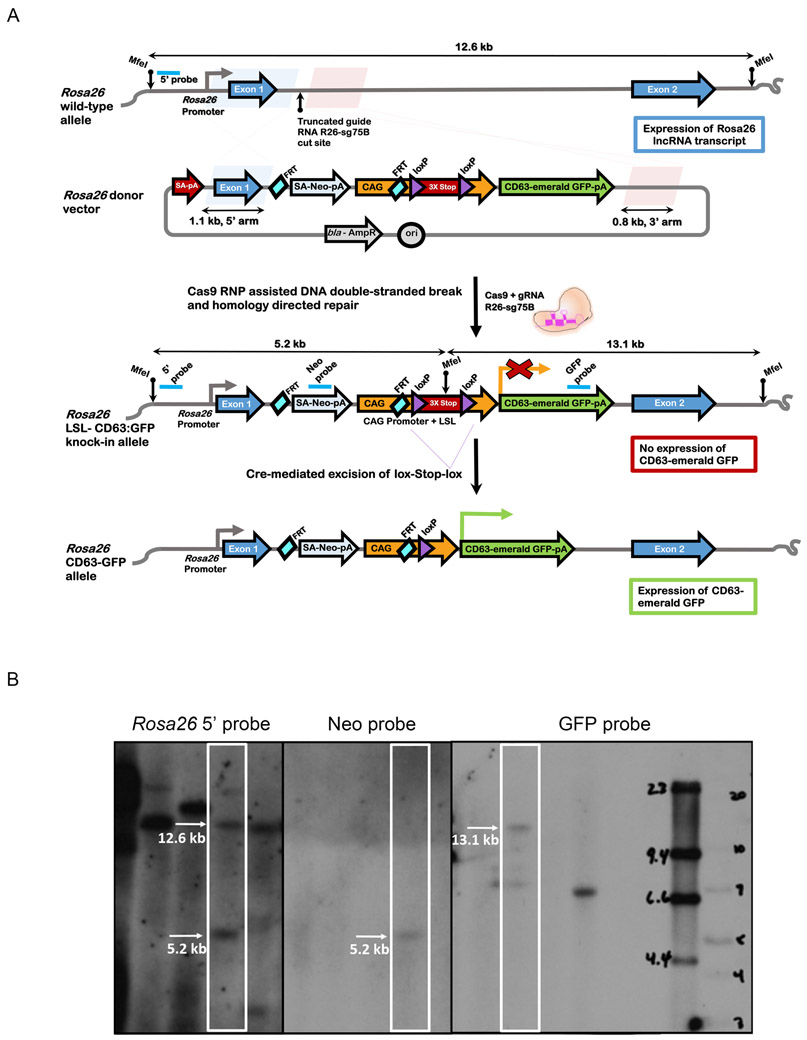
Fig 2. Generation of Rosa26LSL-CD63emGFP mice.
(A) Strategy for knock-in of a conditional CD63-emGFP transgene into a genomic safe harbor site of mouse zygotes. Schematic of wild-type Rosa26 locus and donor vector are shown. The donor vector is designed for CD63:emGFP transgene expression driven by the CAG promoter (CAG) after Cre-mediated excision of the floxed triple SV40 polyA sites. To facilitate insertion of CAG-loxPSTOPloxP-CD63:emGFP cassette into the Rosa26 locus by homology directed repair, ribonucleoprotein complexes containing Cas9 and truncated guide R26-sg75B were directly microinjected into the pronucleus of mouse C57BL/6J zygotes to stimulate a double-stranded DNA break between the 1.1 kb and 0.8 kb homology arms in the donor vector. The locations of MfeI restriction sites and the Southern hybridization probes for detection of the wildtype and knock-in alleles are indicated. (B) Southern blotting analysis from MfeI-digested tail genomic DNA of a representative Rosa26LSL-CD63emGFP founder. An external 5’ hybridization probe detects the Rosa26 wildtype and knock-in alleles of 12.6 kb and 5.2 kb respectively, and indicates that the founder contains both the targeted and wildtype alleles. An internal probe that hybridizes to Neomycin resistance gene (Neo) detects the 5’5.2 kb band for the targeted allele. An internal GFP probe detects the 3’ 13.1 kb band from the knock-in allele.