Figure 3. Structural analyses of the 4E14/BFL-1ΔC interaction.
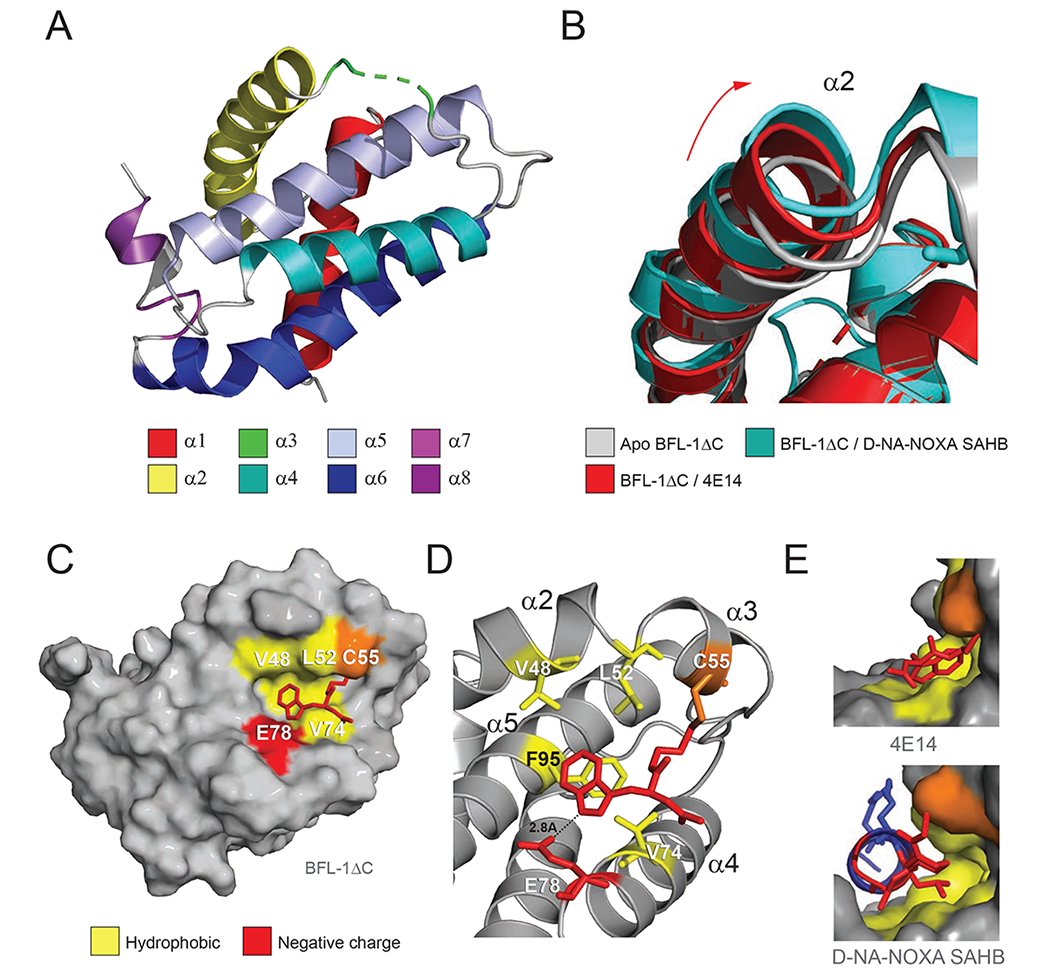
(A) Structure of His6-BFL-1ΔC C4S/C19S when conjugated to 4E14 via C55 (PDB ID: 6VO4). Amino acid residues 55-57 of α3, including the 4E14-C55 conjugate, are not resolved in the structure and instead represented by the green dotted line.
(B) Overlay of the α2 region in the crystal structures of apo BFL-1ΔC (PDB ID: 5WHI), and the complexes between BFL-1ΔC and D-NA-NOXA SAHB (PDB ID: 5WHH) and 4E14 (PDB ID: 6VO4), highlighting the dynamic nature of this region upon small molecule and peptide helix engagement.
(C) Calculated model structure of the 4E14/BFL-1ΔC interaction as determined by covalent docking and molecular dynamics simulations.
(D) Molecular interactions of 4E14 at the docked site on BFL-1ΔC, highlighting engagement of the indole moiety at the hydrophobic p2 region of BFL-1 and proximity of E78 to the indole NH, suggestive of a hydrogen-bonding interaction.
(E) Side views of the interaction between the BH3-binding groove of BFL-1 and 4E14 (top) and D-NA-NOXA SAHB (PDB ID: 5WHH) (bottom), demonstrating the covalent bond between C55 and the respective compounds, in addition to engagement of the disulfide linker (top) and D-nipecotic acid moiety (bottom) with the cryptic site that forms upon ligand-target interaction.
See also Figure S2.
