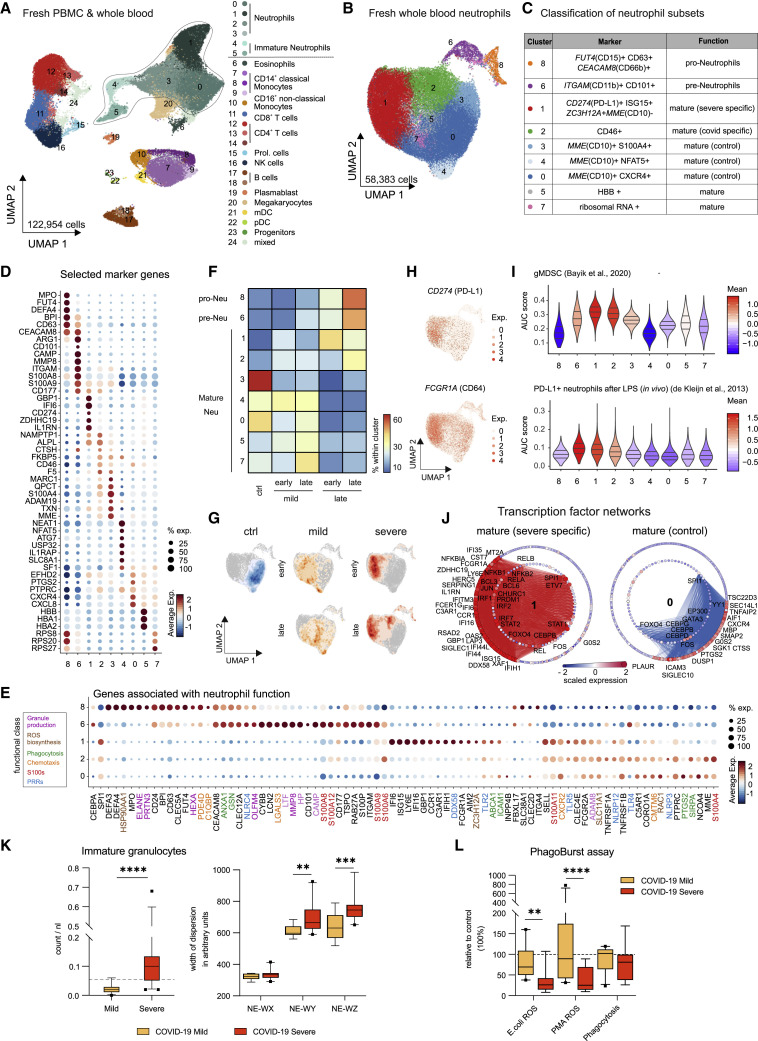
Figure 7.
Immature and Dysfunctional Whole-Blood Neutrophils in Severe COVID-19
(A) UMAP of 35 fresh blood samples from cohort 2 (122,954 cells, PBMCs, and whole blood): controls (n = 17), mild COVID-19 (early, n = 3; late, n = 3) and severe COVID-19 (early, n = 3, late = 9). Clusters defined by Louvain clustering. Cell types assigned based on reference-based cell type classification (Aran et al., 2019) and marker gene expression (Table S4).
(B) UMAP visualization of neutrophils (58,383 cells; 34 whole blood samples, cohort 2): controls (n = 16), mild COVID-19 (early, n = 3; late, n = 3), and severe COVID-19 (early, n = 3; late, n = 9). Clusters defined by Louvain clustering (Table S4).
(C) Nomenclature and marker genes for each neutrophil cluster from (B).
(D) Dot plot of selected marker genes for each neutrophil cluster from (B).
(E) Dot plot of genes from different functional classes (based on literature research). Clusters 8, 6, 1, and 2 are specific for severe COVID-19, cluster 0 represents homeostatic mature neutrophils from controls.
(F) Heatmap divided by disease severity and stage (early versus late) showing the proportion of each patient group for each cluster.
(G) Density plot of cell frequency by disease severity and stage (early versus late) overlaid on the UMAP of the neutrophil space.
(H) UMAP visualization showing scaled expression of CD274 (PD-L1) and FCGR1A (CD64).
(I) Violin plots showing AUCell-based enrichment as AUC scores of gene signature from granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells (Bayik et al., 2020) and PD-L1hi neutrophils after LPS exposure (de Kleijn et al., 2013) in neutrophil clusters from (B). Horizontal lines: median of the respective AUC scores per cluster and 0.25 and 0.75 quantiles.
(J) Network representation of marker genes and their predicted upstream transcriptional regulators for neutrophil clusters 1 (mature/COVID-19 severe-specific) and 0 (mature/control-specific). Edges in cluster color: predicted transcriptional regulation. TFs (inner circle) and their predicted target genes (outer circle): nodes, sized, and colored according to scaled expression level across all clusters. Selected genes and TFs labeled based on connectivity and literature mining.
(K) Box and whisker (10-90 percentile) plots representing the hematological analyses (whole blood, cohort 1): mild (n = 11), severe (n = 21) COVID-19. Analytes, measured by flow cytometry in white blood cell differential channel, included absolute counts of immature granulocytes (IG, dotted line: upper limit of reference range) and width of neutrophil cytometric dispersions (NE-WX, dispersion of side scatter; NE-WY, dispersion of side fluorescence light; NE-WZ, dispersion of forward scatter). Mann Whitney test applied to IG count analysis and mixed-effect-analysis and Sidak’s multiple comparison test to NE-WX, NE-WY, and NE-WZ analyses.
(L) Box and whisker (10–90 percentile) plots of E. coli- and PMA-induced neutrophil oxidative burst (reactive oxygen species [ROS] production) and phagocytosis of whole blood samples (cohort 1; mild, n = 10; severe [n = 8] COVID-19) in comparison to controls measured by flow cytometry. Dotted line: relative level of controls run in the assay. Mixed-effect-analysis and Sidak’s multiple comparison test. ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.