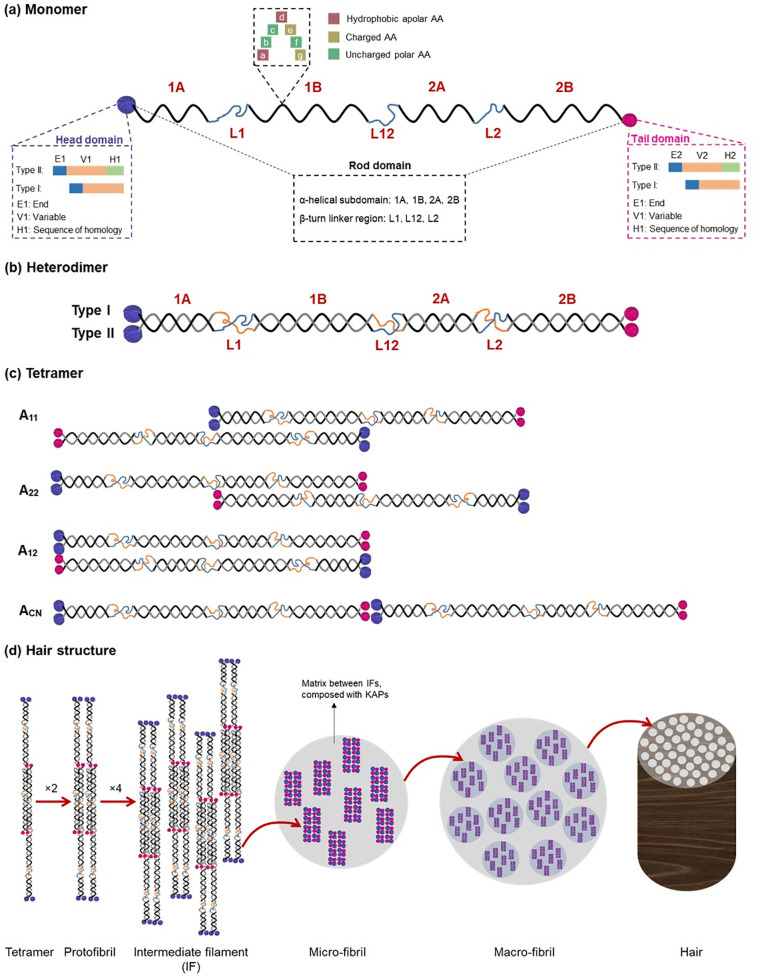
Fig. 1.
α-keratin secondary structure. (a) Monomer structure made up of three parts: head domain (N-terminal domain), rod domain (α-helical domain) and tail domain (C-terminal domain). In addition, the repeating heptad pattern in α-helix is labeled from “a-g” shown in different colors; (b) Heterodimer structure formed from two monomers (one type I keratin monomer and one type II keratin monomer) in parallel alignment; (c) Two heterodimers assembled into a tetramer in four different ways: A11, A22, A12, ACN (Chou and Buehler, 2012); (d) The composition of hair: two tetramers associate into a protofibril, four protofibrils combine into intermediate filament (IF). The IFs are surrounded by sulfide-rich keratin-associated proteins (KAPs).