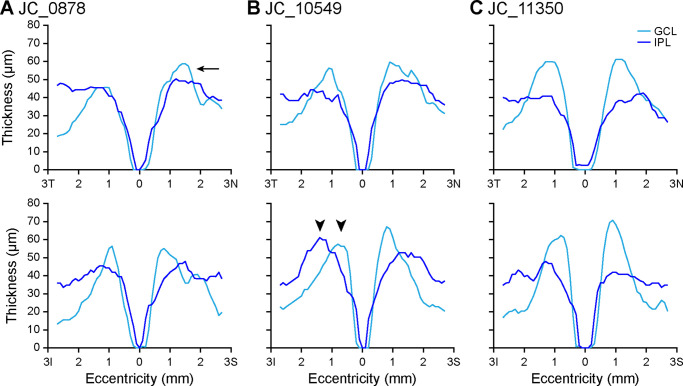
Figure 4.
GCL and IPL thickness topography varies among control participants. Some participants, such as JC_0878 (A), have GCL thickness that exceeds IPL thickness at the foveal rim in the nasal quadrant (arrow), although this may not be the case in the temporal quadrant. This is present in the inferior quadrant in all but seven control eyes, and in the superior quadrant in all but two control eyes. Other participants, such as JC_10549 (B), show a pronounced lateral separation between the maximum GCL thickness and maximum IPL thickness, particularly in the inferior quadrant (arrowheads). Finally, some participants, such as JC_11350 (C), show much greater maximum GCL thickness relative to maximum IPL thickness that is evident in all quadrants. Eccentricity directions are labeled temporal (T), nasal (N), inferior (I), or superior (S).