Figure 1.
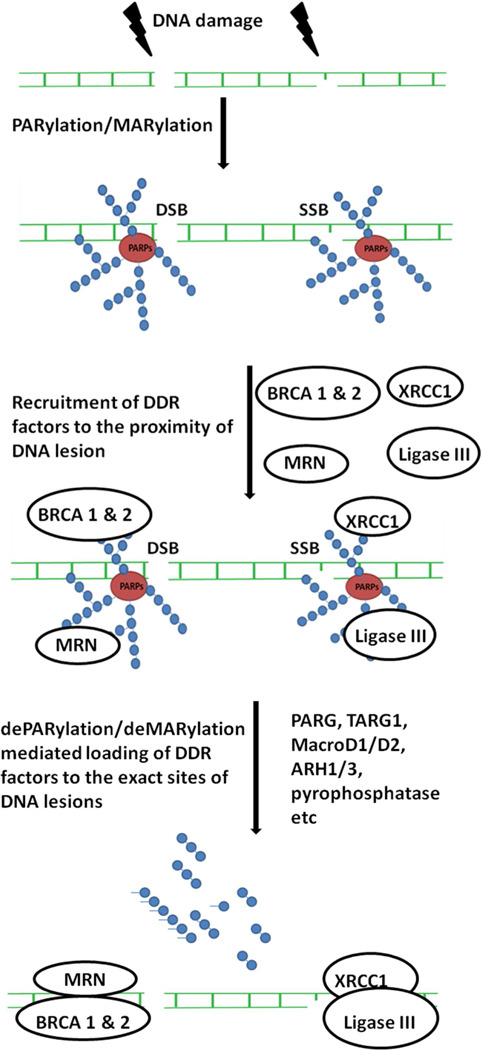
Schematic diagram showing that DNA damage-induced PARylation and dePARylation are sequential steps to mediate the recruitment of DDR response proteins. Both single-stranded (SSB) and double-stranded (DSB) breaks on the target DNA are shown. All the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs) are represented as a single color bubble along with the attached PAR chains. Branched, linear PAR chains and mono-ADPR moieties attached to the PARPs are shown. The DNA damage response (DDR) proteins are recruited to the vicinity of the DNA breaks by the ADP-ribosylation. The ADP-ribosylation signals are removed by dePARylation/deMARylation enzymes as shown leading to the recruitment of DDR proteins to the actual damaged site.
