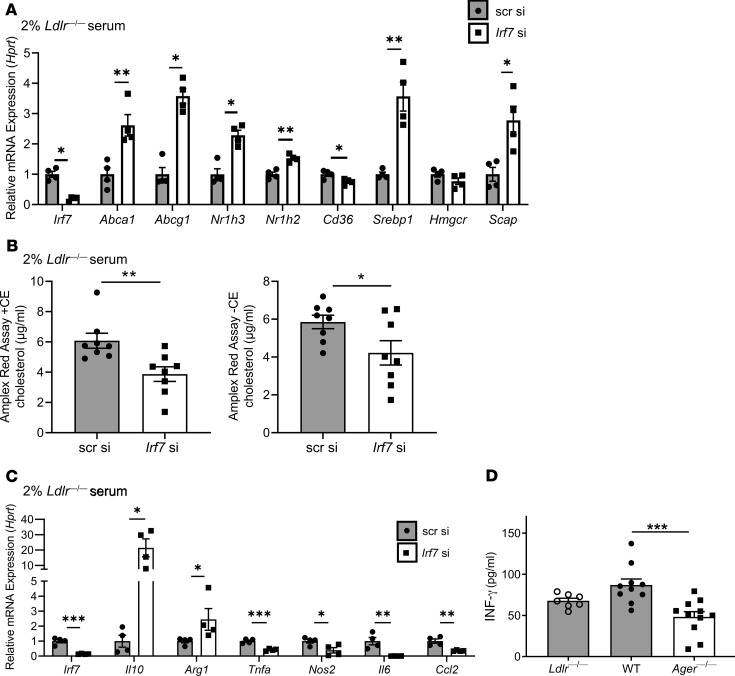
Figure 7. IRF7 regulates macrophage cholesterol content and inflammation.
(A) The expression level of genes involved in cholesterol metabolism after 48 hours of Irf7 or scrambled (75 nM) in WT BMDMs in the presence of a hyperlipidemic environment (2% serum of Ldlr—/— mouse fed a Western diet). N = 4 mice/group. (B) Cellular total cholesterol (left) and free cholesterol (right) content measured using the Amplex Red Cholesterol Assay Kit containing cholesterol esterase or lacking cholesterol esterase (CE), respectively, in WT BMDMs after 48 hours of Irf7 or scrambled (75 nM), in the presence of a hyperlipidemic environment. N = 8 mice/group. (C) The expression level of genes involved in inflammatory processes after 48 hours of Irf7 or scrambled (75 nM) in WT BMDMs in the presence of a hyperlipidemic environment. N = 4 mice/group. (D) Plasma IFN-γ levels were measured by ELISA in diabetic Ldlr—/— donor and WT or Ager—/— diabetic recipient mice 5 days after transplantation. Ldlr—/— diabetic donors (N = 7), WT diabetic recipients (N = 10), and Ager—/— diabetic recipients (N = 11). Mean ± SEM. Unpaired t test or Mann-Whitney U test was performed to assess the difference in A–C depending on the normality of data. One-way ANOVA with post hoc Holm-Šídák multiple comparisons test was used in D. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.