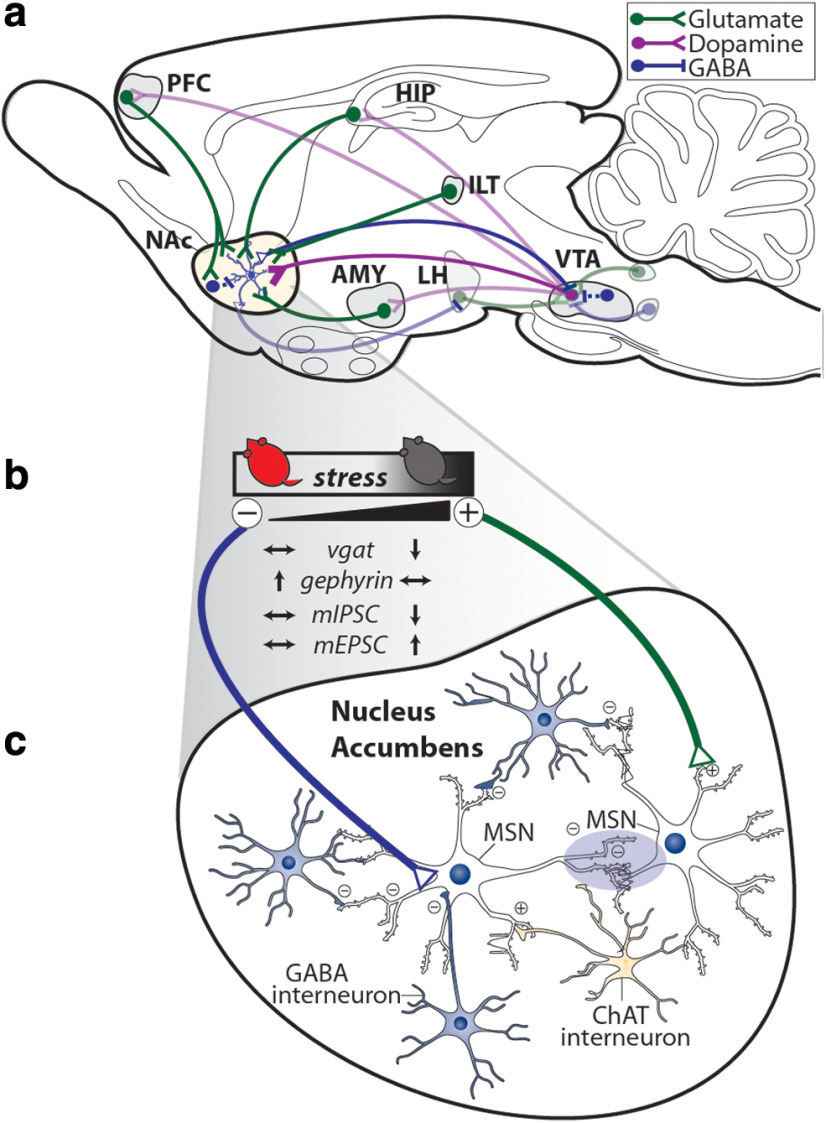
Figure 6.
Model of inhibitory and excitatory synaptic changes in the NAc after CSDS. a, Overview of mesolimbic dopamine circuitry in the mouse brain with glutamatergic (green), dopaminergic (purple), and GABAergic (blue) projections to NAc shown from primary input regions. VTA neurons may release glutamate in addition to dopamine. b, Summary of changes to synaptic plasticity in NAc with increasing susceptibility to stress. c, Stress promotes shifts in NAc excitatory and inhibitory tone with susceptible mice characterized by an overall increase in glutamatergic synapses and a decrease in GABAergic synapses. In addition to receiving inhibitory inputs from different populations of NAc interneurons, MSNs synapse on each other to form an intricate inhibitory microcircuit within NAc.