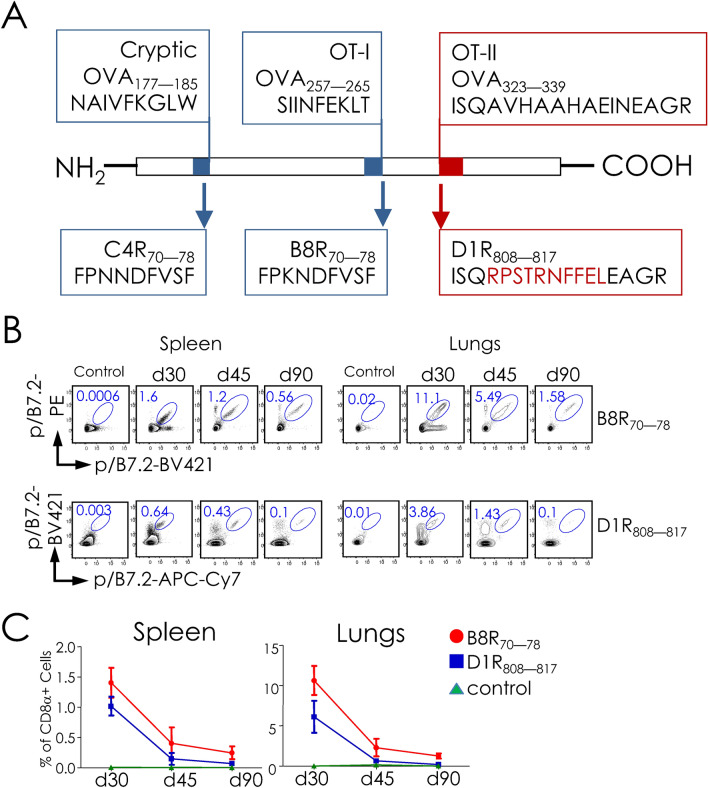
Figure 6.
Intranasal vaccination with rOVA-3 plus αGalCer elicits CD8+ T cell responses. (A) Schematics of OVA (rOVA-3) construct in which the original cryptic, OT-I and OT-II epitopes were replaced with C4R70–78, B8R70–78 and D1R808–817 epitopes, respectively. rOVA-3 containing a C-terminal hexa-histidine tag was constructed by gene synthesis and cloned into pET24a for expression in E. coli. (B,C) B7.2tg mice were primed i.n. with rOVA-3, which contains the D1R808–817 and B8R70–78 epitopes, mixed with αGalCer or αGalCer alone as the control without rOVA-3. After 14 days, primed mice were similarly boosted. Spleens and lungs were harvested on day 30, 45, and 90 after boost. D1R808–817 and B8R70–78 specific CD8+ T cell responses were monitored using epitope-specific pB7.2 tetramers as in Fig. 1. (B) Representative contour plots show D1R808–817- and B8R70–78-specific CD8+ T cells derived from 2–3 independent experiments with two mice in each group/time point. Numbers represent frequency of indicated peptide-specific D1R808–817 and B8R70–78 specific CD8+ T cells at the indicated time points. (C) Frequency (% of CD8+) of D1R808–817- and B8R70–78-specific CD8+ T cells defined by pB7.2 tetramer staining in subunit vaccinated splenocytes and lung leukocytes. Data are cumulative mean ± sem; day 30 (n = 6), day 45 (n = 4), day 90 (n = 4) or control (n = 4).