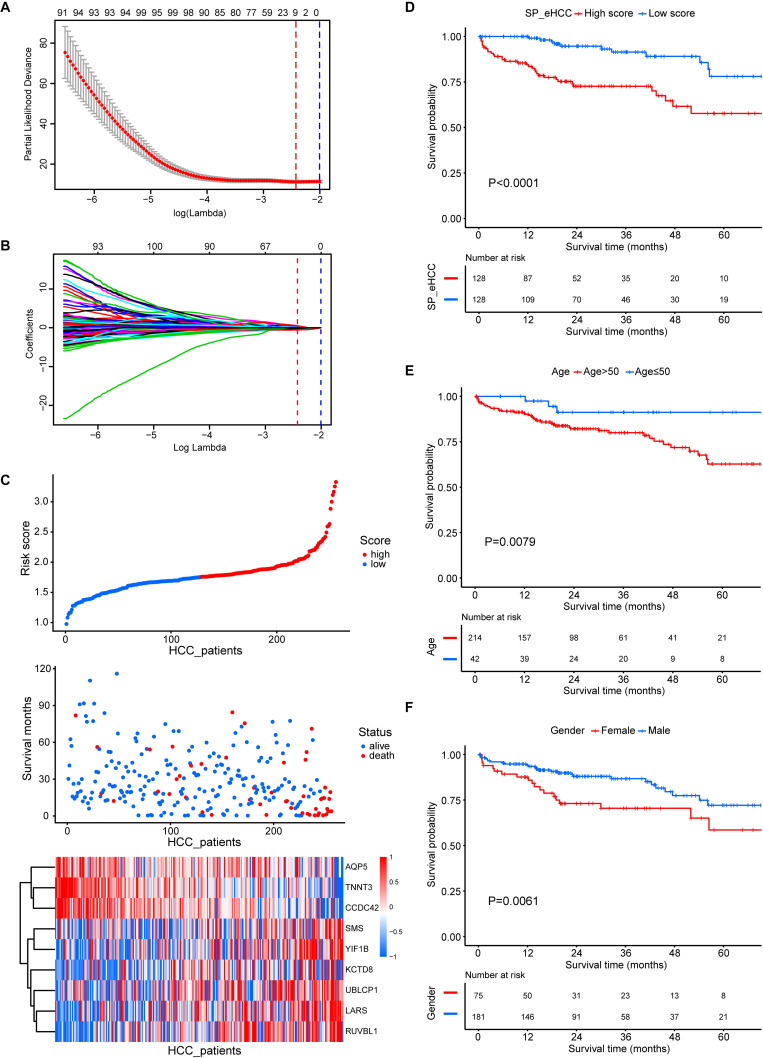
FIGURE 4.
Prognostic significance of the SP.eHCC model and other clinical parameters in early stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). (A,B) Lasso Cox analysis identified nine genes at lambda with minimum partial likelihood deviance (red dotted line) that correlated with the overall survival of early stage HCC patients in the merged cohort (GSE76427, TCGA_GTEx, and ICGC). The red vertical dashed lines indicate the lambda min. (C) The relationship between the risk score of overall survival and the expression of nine genes (AQP5, TNNT3, CCDC42, SMS, YIF1B, KCTD8, UBLCP1, LARS, and RUVBL1) in the SP.eHCC model was shown in the risk score distribution (top), scatter plot of survival status (middle), and heatmap of the prognostic 9-gene signature (bottom) in patients with HCC. The pseudocolors on the right of the heatmap plot represent expression levels from low to high on a scale from –1 to 1, ranging from a low correlation power (white) to high (blue, or red). (D–F) Kaplan–Meier curves of overall survival for 256 early stage HCC patients with different clinical parameters including SP.eHCC, Age, and Gender. HCC patients with relatively low-risk scores had longer mean survival times than patients with relatively high-risk scores (p < 0.0001). Patients aged ≤ 50 had longer mean survival times than patients aged > 50 (p = 0.0079). Male patients had longer mean survival times than female patients (p = 0.0061).