Fig. 3.
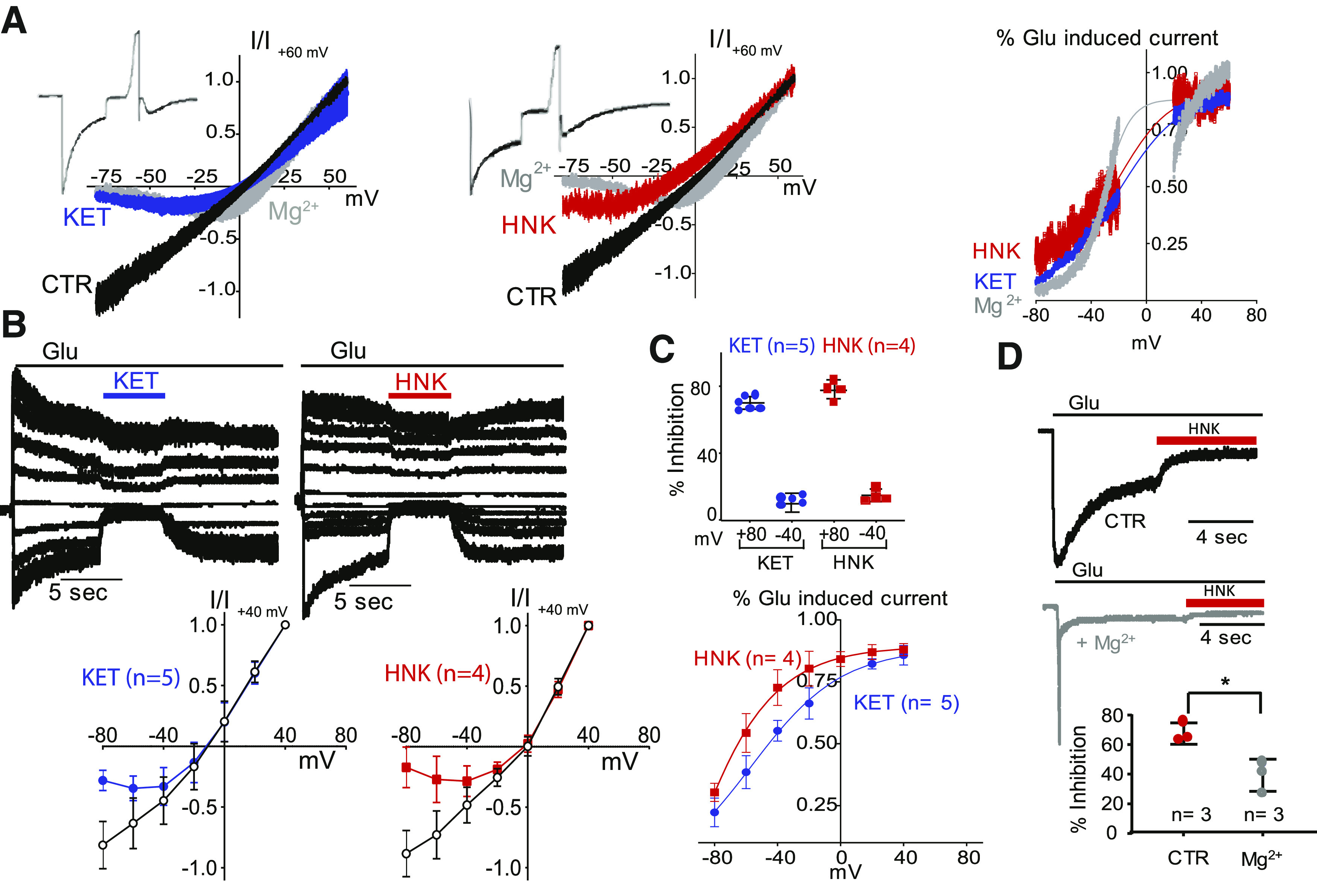
Voltage dependence of NMDA receptor current inhibition by KET, HNK, and Mg. N1/N2A currents were elicited with glutamate (pH 7.2), without (CTR, black), and with modulators applied onto the steady-state portion of the response: KET (10 µM, blue), HNK (500 µM, red), or Mg (1 mM, gray). (A) Exemplary steady-state currents recorded while ramping the holding potential (left, middle) and calculated fractional inhibition relative to membrane voltage (right). (B) Exemplary currents recorded sequentially at several holding potentials (top-left and middle panels) and calculated current-voltage (I/V) plots (below). (C) Calculated percent inhibition of N1/N2A currents at two holding potentials (top-right panel) and calculated fractional inhibition (bottom-right panel). (D) Reduced HNK inhibition of N1/N2A currents by Mg; * P = 0.02 (unpaired Student’s t test).
