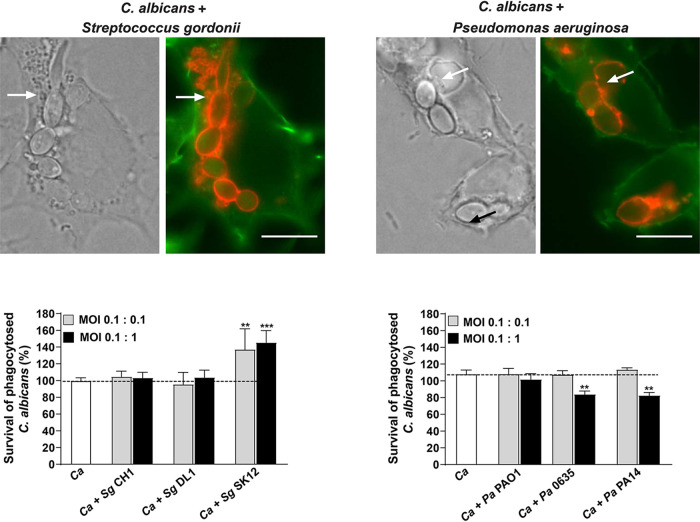
FIG 1.
S. gordonii SK12 strain increases C. albicans survival in macrophages, while P. aeruginosa 0635 and PA14 decrease C. albicans survival. (Upper panels) Phagocytosed C. albicans and bacterial species by murine RAW 264.7 macrophages were evaluated microscopically after 30 min of incubation. Macrophages were stained with phalloidin (green) and phagosomes were immunostained for LAMP1 (red). White arrows indicate phagocytosed S. gordonii SK12 (left) and P. aeruginosa 0635 (right). Scale bar, 10 μm. (Bottom panels) Macrophages were infected with C. albicans and S. gordonii CH1, DL1, and SK12 strains (left) or P. aeruginosa PAO1, 0635, and PA14 strains (right) at an MOI of 0.1:0.1 (gray bars, 0.1 C. albicans:0.1 bacteria) or an MOI of 0.1:1 (black bars, 0.1 C. albicans:1 bacteria). After 3 h of coincubation, macrophages were lysed, and internalized C. albicans was released and plated on antibiotic supplemented agar to remove all bacteria and obtain C. albicans CFU. Survival was calculated as follows: (recovered C. albicans CFU from macrophages/total number of phagocytosed C. albicans) × 100. Coincubation with S. gordonii SK12 significantly increased C. albicans survival, while P. aeruginosa 0635 and PA14 significantly decreased C. albicans survival. Means ± the standard deviations (SD) of at least three independent experiments carried out in duplicate are shown. Significance was obtained using one-way ANOVA with post ad hoc Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test (**, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001). Labels: Ca, C, albicans; Sg, S. gordonii; Pa, P. aeruginosa.