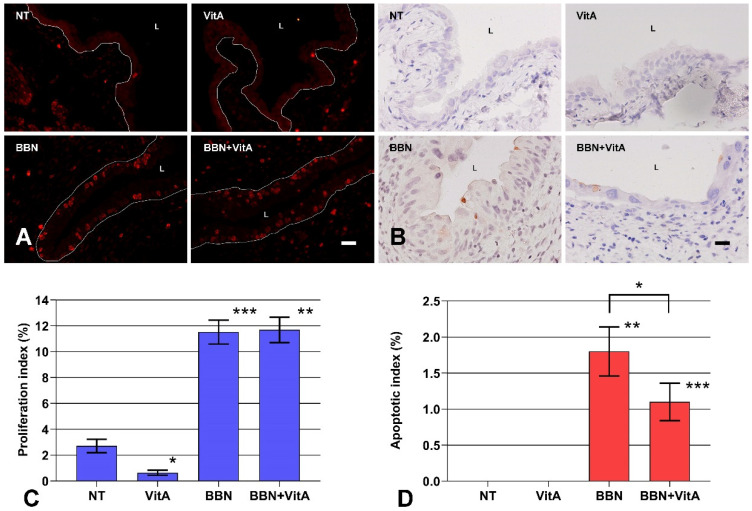
Figure 4.
Proliferation and apoptosis of urothelial cells. (A) Ki-67 immunofluorescence (red) for identification of proliferating cells. Red nuclei are Ki-67 positive nuclei from proliferating cells; white line depicts the location of basal lamina. L, lumen. Scale bar = 50 μm. (B) Active caspase-3 immunohistochemistry (brown) for identification of apoptotic cells. Brown cells are active caspase-3 positive cells dying via apoptosis. Scale bar = 50 μm. (C) Proliferation indices of urothelial cells in NT (n = 6), VitA (n = 6), BBN (n = 12), BBN + VitA (n = 12). Statistically significant differences (tested by ANOVA, F-test, and two-sided Student’s t test) were determined between NT and VitA (* p = 0.0062) and between NT and BBN (*** p = 2.22 × 10−9) and VitA and BBN + VitA (** p = 3.98 × 10−9). There was no statistically significant difference between BBN and BBN + VitA; (D) apoptotic index of urothelial cells in NT (n = 6), VitA (n = 6), BBN (n = 12), BBN + VitA (n = 12). Statistically significant differences (tested by ANOVA, F-test, and two-sided Student’s t test) were determined between NT and BBN (** p = 0.0032) and VitA and BBN + VitA (*** p = 0.00047), and between BBN and BBN + VitA (* p = 0.049).