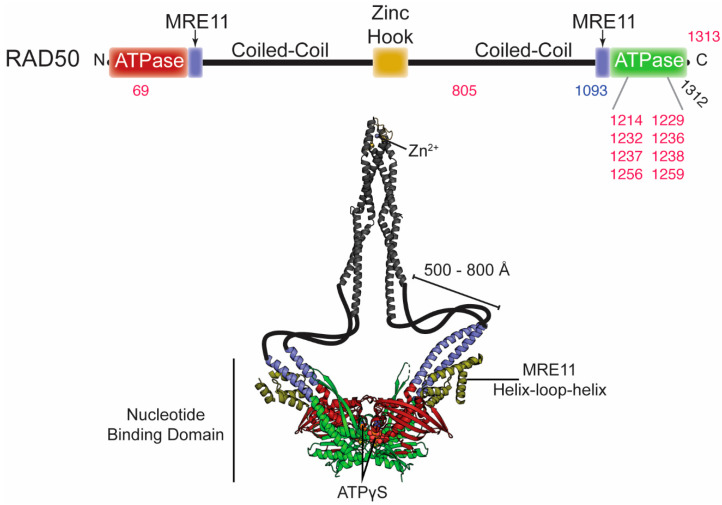
Figure 3.
Disease-associated mutations in RAD50. Top, domain architecture of RAD50. The numbers indicate the position of mutations outlined in the text and Table 2. Red and blue numbers correspond to mutations associated with cancer and NBSLD, respectively. The two arrows above indicate the positions where MRE11 binds. Bottom, crystal structures of the dimer RAD50 nucleotide binding domain in complex with the MRE11 helix-loop-helix domain from C. thermophilum (PDB ID: 5DA9) and the dimer zinc hook domain from H. sapiens (PDB ID: 5GOX). This is the ATPγS-bound “closed” conformation of Rad50. The majority of the coiled-coil domain is absent from these structures, so it is was cartooned in to connect the two structures and is not to scale.