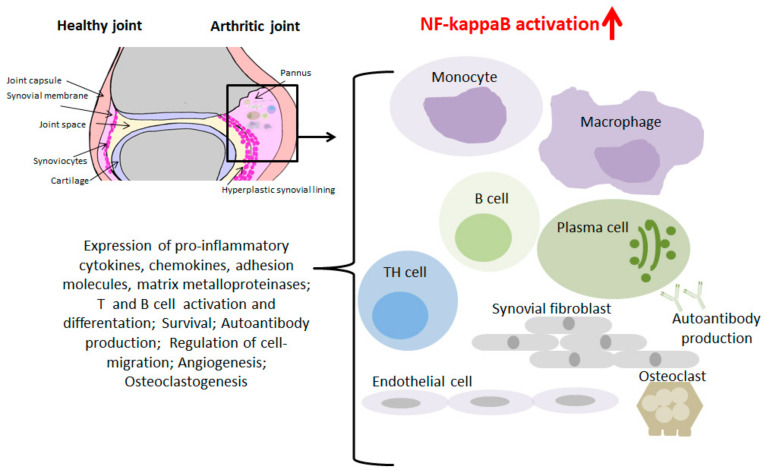
Figure 2.
Role of NF-kappaB in RA. A Healthy and an arthritic joint is presented. Monocytes/macrophages, TH cells, B cells, plasma cells, synovial fibrobasts, endothelial cells, and osteoclasts contribute to RA pathogenesis. Induction of NF-kappaB target genes promotes inflammation leading to cartilage and bone destruction.