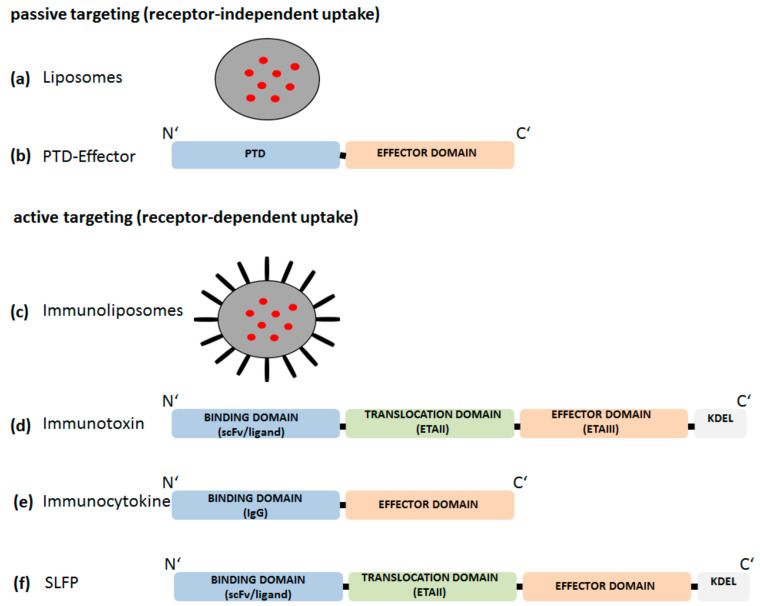
Figure 4.
Tools for “passive” or “active” targeting. (a) non-specific uptake (passive targeting) of liposomes (grey circles) followed by intracellular release of encapsulated substances (red circles). (b) non-specific uptake of an effector molecule coupled to a protein transduction domain (PTD). (c) specific uptake (active targeting) of immunoliposomes (IP). Whole antibodies, ligands, or single chain variable fragments (scFv) (black bars) are coupled to the surface of liposomes (grey circles). IP release their encapsulated substances (red circles) after receptor-mediated uptake. (d) Recombinant modular proteins consisting of a specific binding domain (ligand or scFv), a translocation domain (ETAII) and an effector domain for cell killing (ETAIII). The KDEL motif is included for Golgi to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) transport. (e) Immunocytokines contain an IgG binding domain and an effector domain. (f) Sneaking ligand fusion proteins (SLFPs) are recombinant modular proteins consisting of a specific binding domain (ligand or scFv), the ETAII translocation domain (ETAII) and an effector domain for intracellular modulation of signaling pathways.