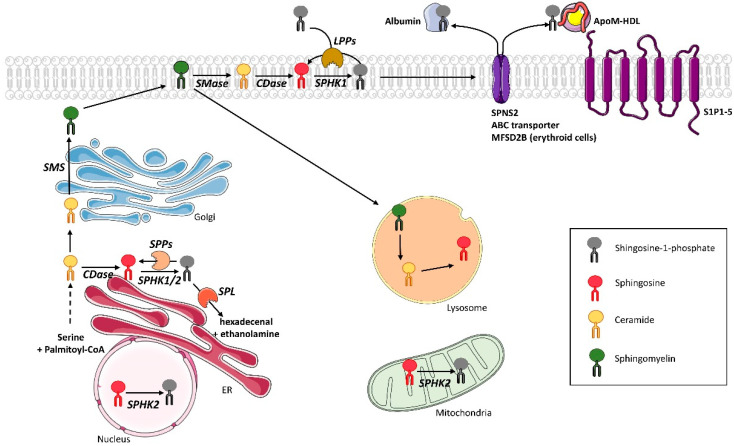
Figure 1.
Sphingosine-1-phosphate metabolism in mammals. Sphingolipid de novo synthesis is initiated in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), starting by the condensation of serine and palmitoyl-coA followed by a cascade of enzymatic reactions to produce ceramide. In the ER, ceramide is deacylated by neutral CDase into sphingosine. Sphingosine is phosphorylated to produce S1P by SphK1/2. Produced S1P can be either dephosphorylated back to sphingosine by ER resident SPPs, or irreversibly transformed into hexadecenal and phosphoethanolamine by S1P lyase. Ceramide is transported to the Golgi apparatus to be transformed into SM, which will reach the plasma membrane. In the plasma membrane, SM can be transformed into ceramide through the action of SMases. Ceramide will then be deacylated by acidic CDase to give sphingosine that will be phosphorylated into S1P by SphK1. Produced S1P can be dephosphorylated by ecto-LPPs. S1P can also be secreted through ABC, SPNS2, and MFSD2B transporters in extracellular space to activate S1P receptors. Extracellular S1P can also be transported by either albumin or ApoM/HDL. The latter can activate S1P receptors. SM can be endocytosed to be recycled into ceramide and sphingosine inside lysosomes. SphK2 can catalyze S1P production in the mitochondria and the nucleus. ABC: ATP-binding cassette. CDase: ceramidase. ER: endoplasmic reticulum. HDL: high density lipoproteins. MFSD2B: Major Facilitator Superfamily Domain Containing 2B. S1P: sphingosine-1-phosphate. SM: sphingomyelin. SMase: sphingomyelinase. SphK: sphingosine kinase. S1P1-5: S1P receptor 1 to 5. SPNS2: Spinster homolog 2. SPP: Sphingosine-1-phosphate phosphohydrolase.