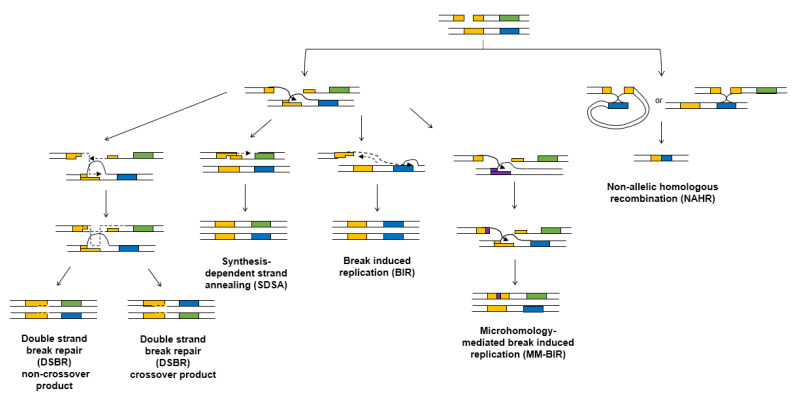
Figure 2.
Mutagenic outcomes of homologous recombination. All types of homologous recombination begin with resection to form single-stranded DNA, followed by RAD51-mediated strand invasion. SDSA and DSBR usually use the sister chromatid as a template but the use of the homologous chromosome can result in loss of heterozygosity (SDSA) or mitotic crossovers (DSBR). BIR involves the formation of a mobile D-loop and produces long, single-stranded DNA tracts. BIR can result in loss of heterozygosity and mutations caused by damage in persistent ssDNA. MM-BIR involves multiple rounds of strand invasion, which can cause insertions of heterologous sequences. NAHR occurs when single-stranded DNA invades into a non-allelic template. NAHR can be intrachromosomal or interchromosomal and results in deletions (shown), duplications, and inversions.