Table 4.
Adjusted Mean Difference in 15-year Change in Cognitive Performance Among Black Participants According to Visit 4 Ethanol Intake Status, Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities, United States, 1987–2013
| Test and Drinking Status at Visit 4 | No. | Baseline Cognitive Score | 15-Year Decline a | Adjusted Mean Difference a,b , c | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | Estimate | 95% CI | Estimate | 95% CI | % d | P for Difference e | ||
| Global factor score z score | 2,342 | −0.73 (0.75) | 0.697 | |||||
| Never drinking | 817 | −0.85 (0.71) | −0.53 | −0.91, −0.15 | 0 | Referent | 0 | |
| Low to moderate drinking | 531 | −0.55 (0.77) | −0.52 | −0.90, −0.14 | 0.01 | −0.10, 0.13 | −2 | |
| Heavy drinking | 78 | −0.62 (0.91) | −0.40 | −0.82, 0.03 | 0.13 | −0.09, 0.35 | −25 | |
| Former drinking | 915 | −0.75 (0.74) | −0.52 | −0.90, −0.14 | 0.01 | −0.09, 0.11 | −1 | |
| Delayed word recall z score | 2,340 | −0.37 (1.11) | 0.814 | |||||
| Never drinking | 816 | −0.39 (1.12) | −0.95 | −1.72, −0.18 | 0 | Referent | 0 | |
| Low to moderate drinking | 530 | −0.31 (1.16) | −0.86 | −1.63, −0.09 | 0.09 | −0.12, 0.31 | −10 | |
| Heavy drinking | 78 | −0.38 (1.13) | −0.79 | −1.62, 0.04 | 0.16 | −0.30, 0.62 | −17 | |
| Former drinking | 916 | −0.38 (1.06) | −0.89 | −1.65, −0.12 | 0.06 | −0.13, 0.26 | −6 | |
| Word fluency z score | 2,334 | −0.39 (1.06) | 0.609 | |||||
| Never drinking | 814 | −0.53 (1.02) | −0.40 | −0.83, 0.03 | 0 | Referent | 0 | |
| Low to moderate drinking | 529 | −0.16 (1.1) | −0.34 | −0.77, 0.10 | 0.06 | −0.06, 0.18 | −16 | |
| Heavy drinking | 77 | −0.28 (1.13) | −0.27 | −0.75, 0.22 | 0.13 | −0.12, 0.38 | −33 | |
| Former drinking | 914 | −0.41 (1.05) | −0.38 | −0.80, 0.05 | 0.02 | −0.08, 0.13 | −6 | |
| Digit symbol substitution z score | 2,325 | −0.97 (0.94) | 0.614 | |||||
| Never drinking | 812 | −1.13 (0.91) | −0.26 | −0.69, 0.17 | 0 | Referent | 0 | |
| Low to moderate drinking | 528 | −0.74 (0.94) | −0.32 | −0.74, 0.11 | −0.06 | −0.17, 0.06 | 21 | |
| Heavy drinking | 77 | −0.75 (1.06) | −0.27 | −0.74, 0.20 | −0.01 | −0.23, 0.22 | 3 | |
| Former drinking | 908 | −0.98(0.92) | −0.32 | −0.74, 0.10 | −0.06 | −0.15, 0.03 | 22 | |
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; SD, standard deviation.
a Multivariable linear regression models adjusted for age, age squared, sex, race-center, educational attainment, diet quality score, physical activity, smoking status, body mass-index, diabetes, history of stroke and the apolipoprotein E 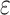 4 allele.
4 allele.
b Estimates were averages from 25 rounds of multiple imputation combined using Rubin’s rule and the variance of a function of the within and between completed data set variances.
c Difference modeled as the follow-up neurocognitive exam (visit 5; 2011–2013) z score minus study baseline (visit 4; 1996–1998) z score. Negative values correspond to greater decline compared with the referent (never drinker).
d Percent, positive values represent % greater decline relative to the referent group.
e P value for t test of equality of mean difference in 15-year change in cognitive performance across visit 4 ethanol intake.
