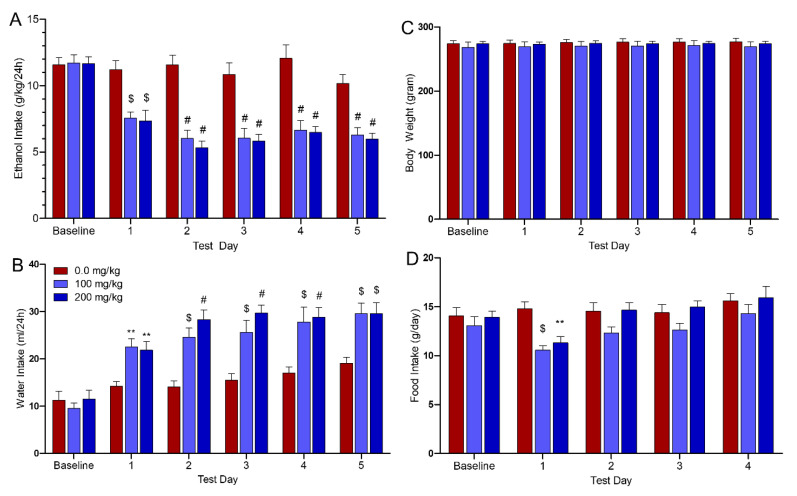
Figure 1.
Effects of ampicillin/sulbactam (AMP/SUL) treatments (100 mg/kg and 200 mg/kg, i.p.) for five consecutive days on (A) Ethanol consumption (g/kg of average body weight/day), (B) Water intake (mL/day), (C) Body weight, and (D) Food intake. Statistical analyses revealed that AMP/SUL consistently reduced ethanol intake with a concomitant increase in water intake. However, there was an increase in water intake on Day 5 as compared to baseline (p < 0.01) in ethanol-control group. While food intake was transiently reduced on the 1st day of treatment, there were no other significant effects of AMP/SUL. In addition, AMP/SUL did not affect body weight. The values are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 9/group), (* p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01, $ p < 0.001 and # p < 0.0001).