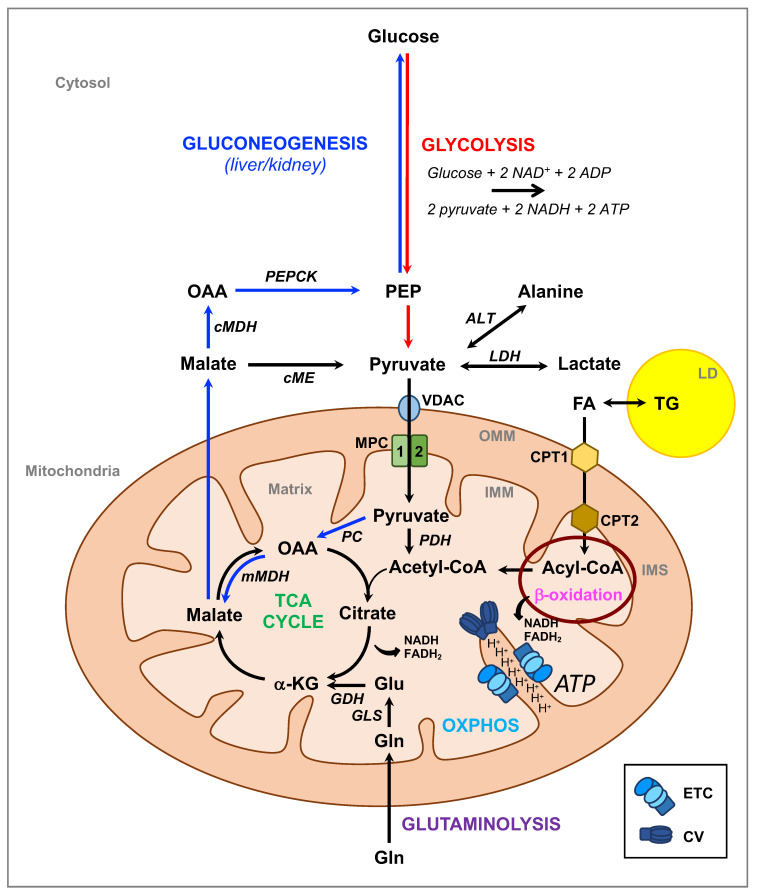
Figure 1.
Metabolic pathways involving mitochondria. In the cytosol, pyruvate is produced through glycolysis, which generates two adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and two reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) molecules per molecule of glucose. Pyruvate can also be produced from oxidation of lactate by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), conversion from alanine by alanine transaminase (ALT), or from malate by cytosolic or mitochondrial malic enzyme (ME). Pyruvate can be imported into mitochondria to be oxidized into acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) by the pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH), which then fuels the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. Import of pyruvate requires the voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC) to cross the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM) and the mitochondrial pyruvate carrier (MPC) to cross the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM). The TCA cycle can also be fueled by glutamine (Gln) through glutaminolysis or by fatty acids (FA) released from lipid droplets (LD) where they are stored in the form of triglycerides (TG). FAs provide acetyl-CoA through FA β-oxidation. The TCA cycle and β-oxidation both generate the reducing equivalents NADH and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FADH2), which transfer electrons to the electron respiratory chain (ETC), generating more than 30 ATP molecules per molecule of glucose. The last reaction is catalyzed by ATP synthase or Complex V (CV). This process requires the presence of oxygen and is known as oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). In the liver and kidney, pyruvate can be converted into oxaloacetate (OAA) by the pyruvate carboxylase (PC), which is then reduced into malate by the malate dehydrogenase (mMDH). Malate is then exported into the cytosol, converted into OAA by malate dehydrogenase (cMDH) and into phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) by PEP carboxykinase (PEPCK) and from there into glucose through several steps, including the reversible steps of glycolysis. IMS: intermembrane space; CPT1: carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1; CPT2: carnitine palmitoyltransferase 2; GDH: glutamate dehydrogenase; GLS: glutamase; α-KG: α-ketoglutarate.