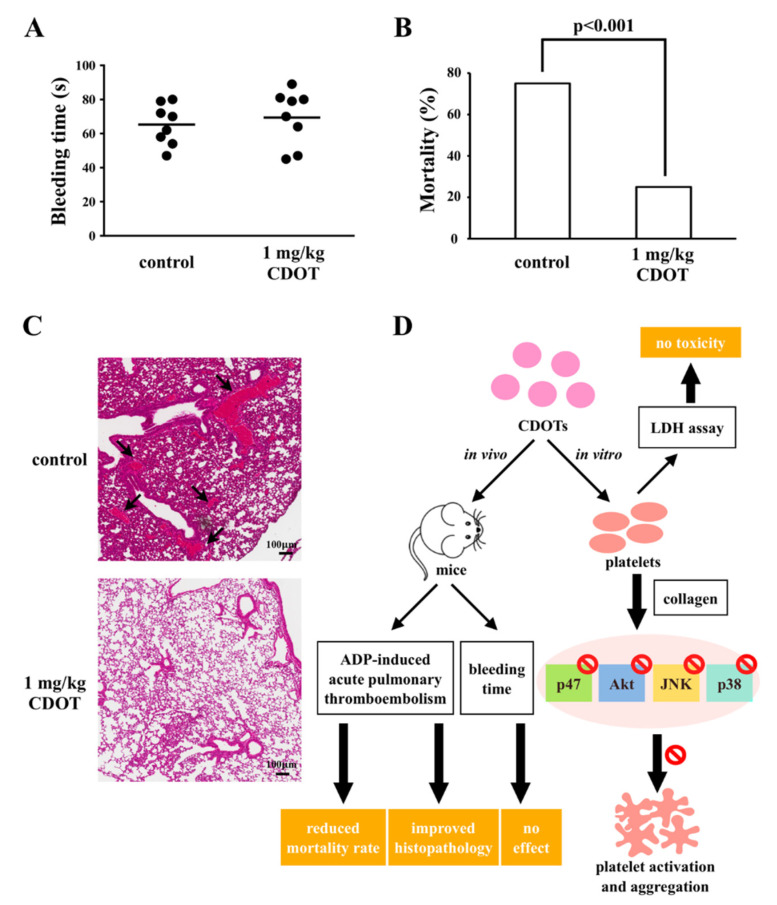
Figure 6.
Effects of CDOTs on tail bleeding time and pulmonary thrombosis in experimental mice. (A) Bleeding time was measured through tail transection after 10 min of intravenous administration of PBS (control) or 1 mg/kg CDOTs. The bleeding time was continuously recorded until no sign of bleeding was observed for at least 10 s. (B) For the study of acute pulmonary thrombosis, PBS (control) or 1 mg/kg CDOTs was intravenously administered to mice, and ADP (0.7 mg/g) was then injected through the tail veins. (C) Pulmonary thrombosis (arrows) was observed by staining lung tissue sections with hematoxylin–eosin. Scale bar: 100 μm. Values represent mean ± SEM (n = 8). (D) Schematic illustration showing the inhibitory effect of CDOTs in human platelets. CDOTs potently inhibit human platelet activation by suppressing PKC activation and Akt, JNK1/2, and p38 MAPK phosphorylation without inducing cytotoxicity. CDOTs reduced the mortality in ADP-induced thromboembolic mice and did not affect bleeding tendency.