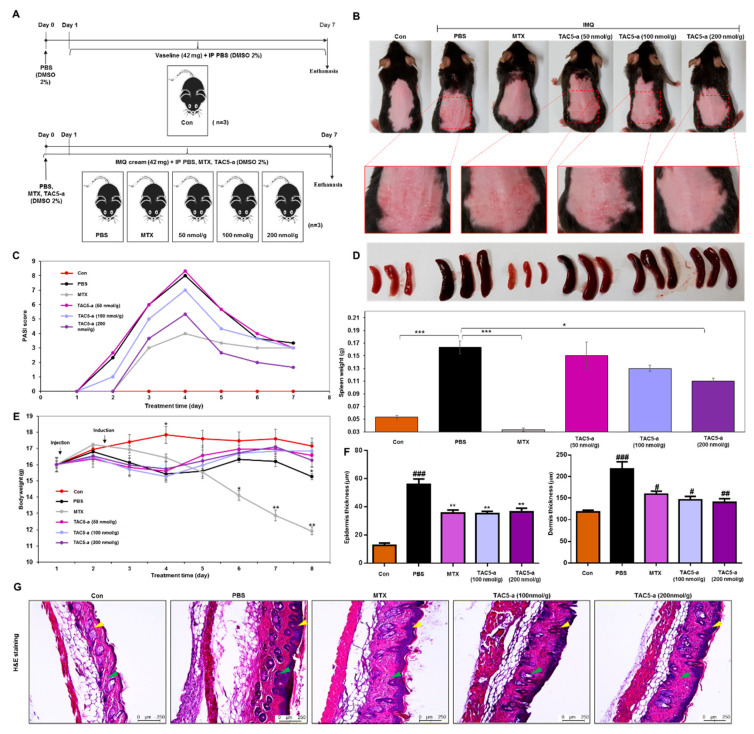
Figure 4.
Effect of TAC5-a in a mouse model of psoriasis. (A) Summary of the experiment for evaluating the therapeutic effect of TAC5-a on a psoriasis mouse model. Psoriasis was induced by applying imiquimod (IMQ) cream (5%) on the shaved back skin of C57BL/6 male mice (n = 3). Mice were treated with daily doses of PBS as a control and 50, 100, and 200 nmol/g of TAC5-a intraperitoneally (IP). Methotrexate (MTX; 20 μg/g) was administered as a positive control from one day before applying IMQ cream as a pretreatment. (B) Photographs of shaved mouse back skin on day 4 to monitor the effect of TAC5-a on psoriasis condition. (C) Scoring of disease severity based on the clinical Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI). Orange, dark blue, and green lines indicate the PASI index of mice treated with TAC5-a at 50, 100, and 200 nmol/g, respectively. (D) Effect of TAC5-a on spleen weight. (E) Body-weight dynamics of mice during the treatment regimen. (F) The thickness of the epidermis and dermis in TAC5-a and MTX (positive control) group. (G) The Histopathological changes of back skin lesions of each group. Skins were stained with hematoxylin and eosin to evaluate the thickness of the epidermis (yellow arrow) and dermis (green arrow) in IMQ-induced psoriasis-like mice. The skin thickness of each group was measured with the Leica DMi8 fluorescence microscope. Data represent mean ± SEM from five skin tissue of each group by two-tailed Student’s t-test, # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.